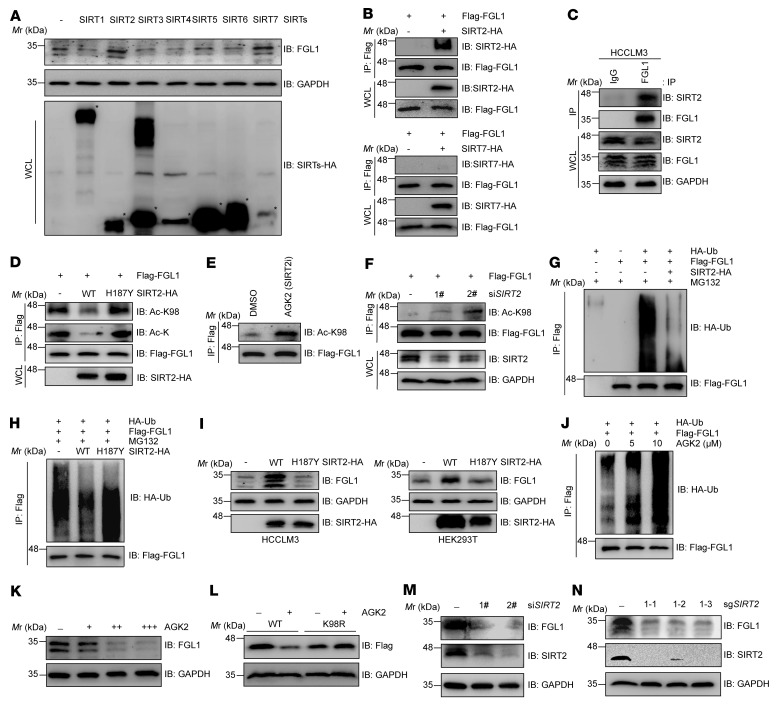
Figure 2. SIRT2 deacetylates and stabilizes FGL1.
(A) IB analysis of endogenous FGL1 in HCCLM3 cells transfected with SIRTs. The interactions between FGL1 and SIRT2 or SIRT7 were determined by co-IP followed by IB analysis. (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-FGL1 and SIRT2-HA or SIRT7-HA as indicated. The interactions between FGL1 and SIRT2 or SIRT7 were determined by co-IP and IB analysis. (C) Endogenous interaction between FGL1 and SIRT2 in HCCLM3 cells was determined by IP and IB analysis. IgG was used as a negative control. (D) HEK293T cells stably expressing Flag-FGL1 were transfected with SIRT2-HA or its catalytic mutant as indicated. The acetylation of FGL1 was analyzed with pan– or site-specific anti–FGL1 acetylation antibodies. (E) HEK293T cells stably expressing Flag-FGL1 were treated or not with AGK2. Site-specific anti–FGL1 acetylation antibodies were used to determine the acetylation of FGL1 by IB analysis. (F) HEK293T cells stably expressing Flag-FGL1 were transfected with or without an siRNA oligonucleotide targeting SIRT2. The knockdown efficiency and the acetylation level of FGL1 were analyzed by IB. (G) IB analysis of FGL1 ubiquitination levels in HEK293T cells transfected with Flag-FGL1, SIRT2-HA, or HA-Ub. (H) IB analysis of FGL1 ubiquitination levels in HEK293T cells transfected with SIRT2-HA or its catalytic mutant. (I) IB analysis of both endogenous and exogenous FGL1 in HCCLM3 or HEK293T cells transfected with SIRT2-HA or its catalytic mutant. (J) IB analysis of FGL1 ubiquitination levels in HEK293T cells transfected with Flag-FGL1 and HA-Ub and treated with or without AGK2. (K) IB analysis of endogenous FGL1 in HCCLM3 cells treated with AGK2 (10–40 μM) for 8 hours. (L) IB analysis of FGL1 in HEK293T cells transfected with WT FGL1 or the K98R mutant under treatment with AGK2 for 8 hours. (M) IB analysis of endogenous FGL1 in WT and SIRT2-KO SMMC-7721 cells. (N) IB analysis of endogenous FGL1 in WT and SIRT2-KO HCCLM3 cells.