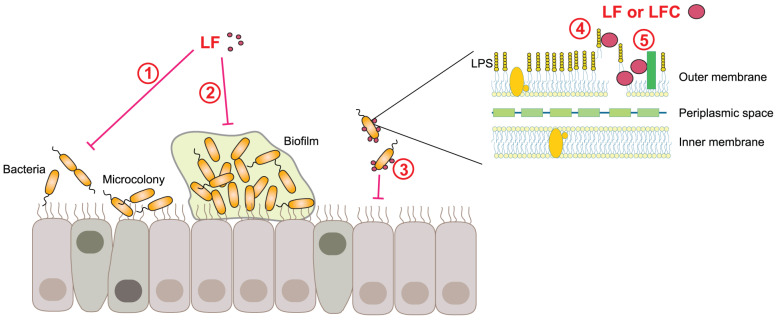
Figure 4.
Antimicrobial actions of LF and LFC. LF has antibacterial activity toward a spectrum of different bacterial pathogens, through iron sequestration, which is bacteriostatic (1), or leads to bacterial twitching that prevents biofilm formation (2). Moreover, via its N-glycans, LF acts as a soluble decoy receptor for invasive pathogens to disrupt their adherence to host cells and cell invasion strategies (3). LF and LFC can cause membrane permeabilization (4) and bind and neutralize bacterial virulence mechanisms, e.g., the type III secretion system of EPEC (5).