FIGURE 3.
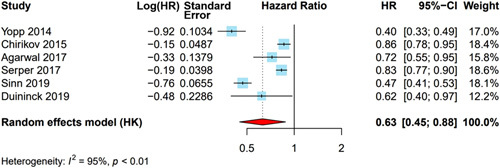
Association between multidisciplinary care and overall survival. Multidisciplinary care was significantly associated with improved survival, with a pooled HR of 0.63 (95% CI: 0.45–0.88); however, there was high heterogeneity (I 2 = 95%, p < 0.01). DerSimonian and Laird method was used for a random effects model.
