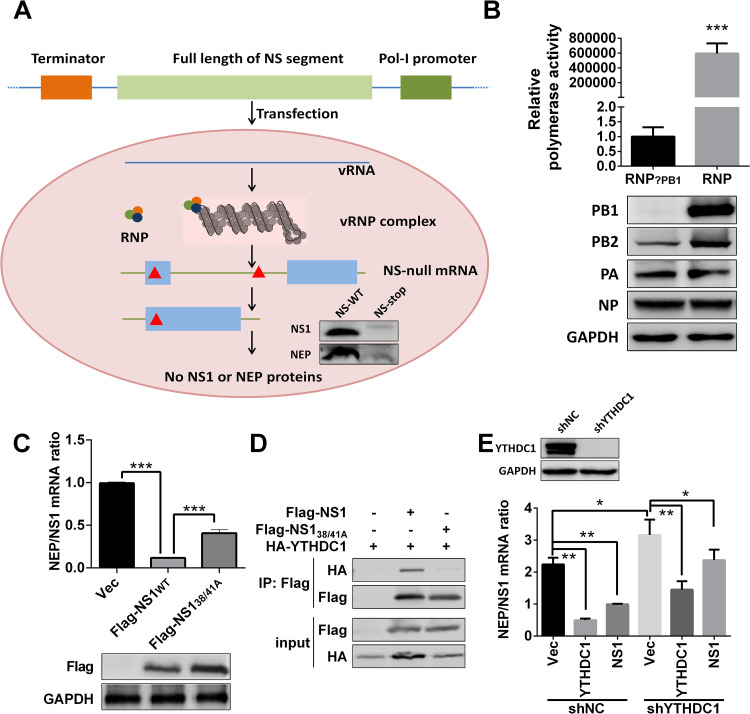
Fig 4. NS1 regulates NS segment splicing through YTHDC1.
(A) Schematic illustration of NS-null minigenome system and detection of specific NS mRNAs. Construction of the pHI NS-null plasmid, which contains multiple stop codons (red triangle). Primers used for NS-null mRNA detection are shown as blue arrowheads. 3P (PA, PB1, PB2). NS-null (two stop codons were mutated at positions 45 and 456, with transcription but not translation). (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated viral RNP reconstitution plasmids (pCDNA-3.1-PB1, -PB2, -PA, and -NP, pPolI-Luc, and Renilla); polymerase activity was measured at 24 h post transfection. Data are presented as the average of three experiments and error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM) (Student t-test; ***, P<0.001). (C) HEK293T cells were transfected with the minigenome system and Flag-NS1 or Flag-NS138/41A for 24 h, total RNAs were extracted and quantified by RT-qPCR with specific primers, and NEP/NS1 mRNA was calculated. Data are presented as the average of three experiments and error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM) (one-way ANOVA; ***, P<0.001). (D) HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h. CoIP assay was performed using an anti-Flag antibody and analyzed by western blotting. (E) YTHDC1 was knocked down by shRNA on HEK293T cells. And indicated plasmids were transfected with the minigenome system, and related NEP/NS1 ratios were detected at 24 hours post transfection. Data are presented as the average of three experiments and error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM) (one-way ANOVA; *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01).