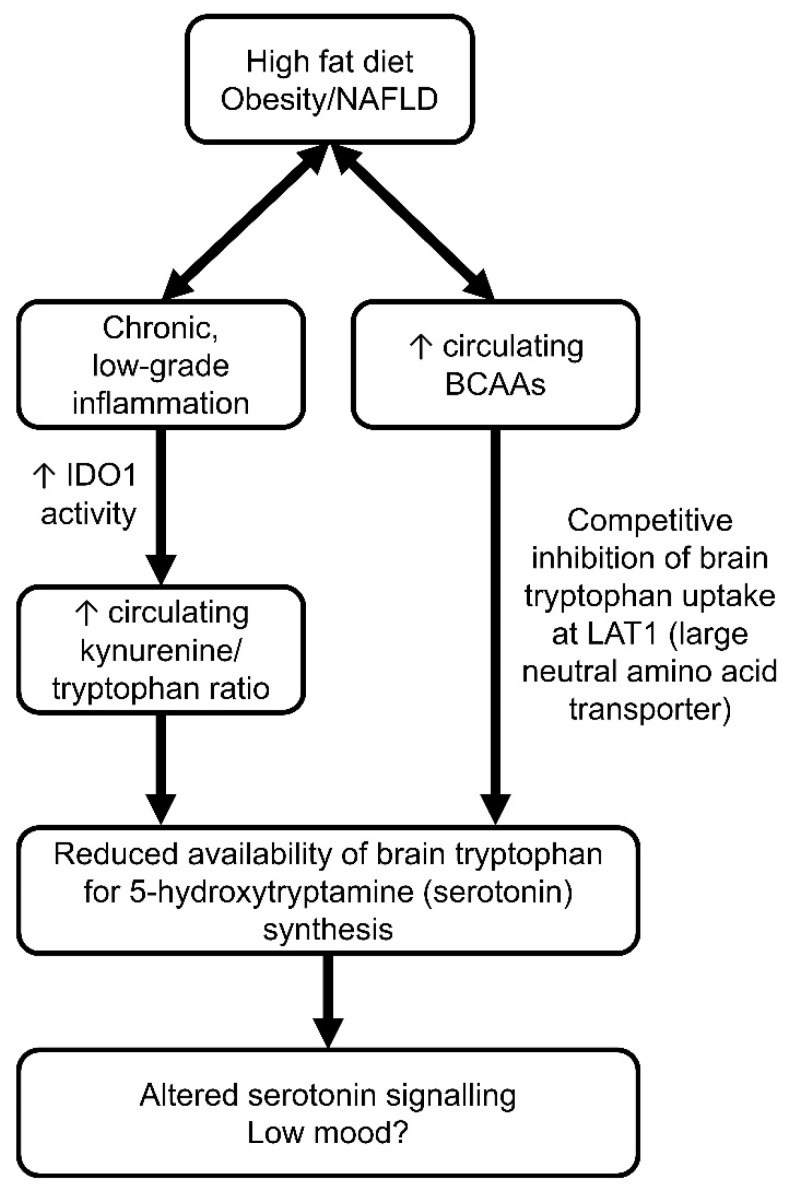
Figure 3.
Potential mechanisms describing how diet-induced metabolic syndrome (obesity/NAFLD) may lead to altered brain plasticity and low mood. On the left side of the flowchart, chronic, low-grade inflammation is thought to upregulate peripheral indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1) activity, leading to increased kynurenine production from tryptophan and reduced brain tryptophan uptake for central serotonin synthesis. On the right, elevated circulating branched-chain amino acids may arise after prolonged high-fat diet feeding. BCAAs compete with tryptophan for the large neutral amino acid transporter (LAT1), reducing brain uptake of tryptophan and central serotonin synthesis. This may lead to altered neurotransmission and low mood. ↑ increase.