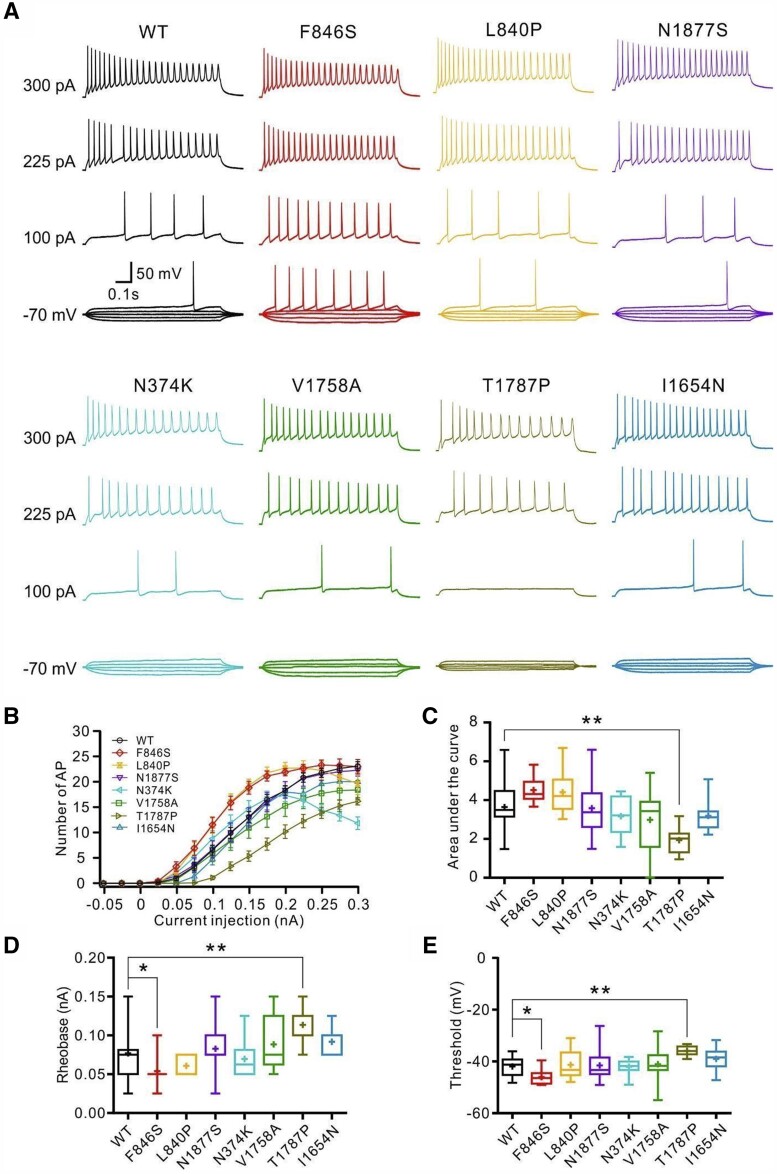
Figure 2.
Effects of SCN8A variants in primary cultured hippocampal mouse neurons in the absence of tetrodotoxin. Neurons were transfected with wild-type or mutant Nav1.6 channels and recorded in the absence of tetrodotoxin. (A) Representative voltage traces of evoked action potentials (APs) in the absence of tetrodotoxin from neurons transfected with wild-type (WT, black) or mutant neurons (colour code indicated in B). (B) Numbers of evoked action potentials plotted versus injected current in the absence of tetrodotoxin. Shown are means ± SEM. (C) Area under the curve for the input-output relationships. The p.(Thr1787Pro) variant shows a significantly decreased area under the curve compared with the wild-type channels. Rheobase (D) and threshold (E) of action potentials were decreased for neurons transfected with the p.(Phe846Ser) variant but increased for neurons transfected with the p.(Thr1787Pro) variant compared with the wild-type channels. Box-and-whisker plots (C–E) show means (plus sign), the 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles, minima and maxima; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test or ANOVA on ranks with Dunn’s post hoc test were performed. Numbers of recorded cells and statistical analysis are provided in Supplementary Table 3.