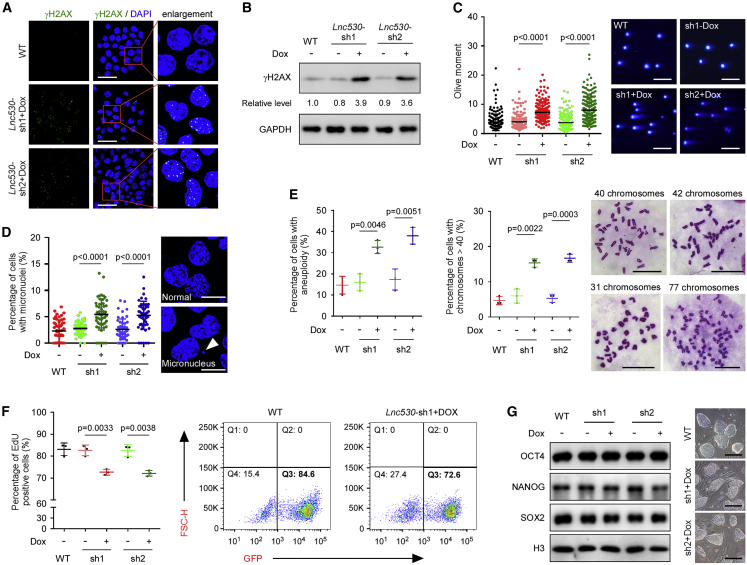
Figure 2.
Loss of Lnc530 causes genomic instability in mESCs
(A and B) Immunostaining (A) and immunoblotting (B) showed that depletion of Lnc530 increased DSB formation as monitored by increased γH2AX level. Scale bars, 40 μm.
(C) Neutral comet assay validated the increased DSB level in Lnc530 KD mESCs. Left panel shows the quantification of comet tail length. Right panel shows representative images. At least 200 tails were analyzed in each group. Scale bars, 400 μm.
(D) More Lnc530 KD mESCs contained micronuclei. Left panel shows the quantification of micronuclei formation. Right panel shows representative images (arrow). At least 50 visual fields containing 1,000 cells were analyzed in each group. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(E) More Lnc530 KD mESCs displayed aneuploidy. Left panel shows the quantification of aneuploidy. Middle panel shows the quantification of aneuploidy with chromosome numbers >40. Right panel shows representative images. At least 150 metaphase spreads were examined in three replications in each group. Scale bars, 20 μm.
(F) Flow cytometry assay showed that the proliferation of Lnc530 KD mESCs was impaired. Left panel shows the quantification result. Right panel shows representative images of flow cytometry.
(G) Immunoblotting showed that the protein expression of core pluripotency regulators SOX2, NANOG, and OCT4 was not changed in Lnc530 KD mESCs (left). Moreover, Lnc530 KD mESCs had normal colony morphology (right). Scale bars, 200 μm. All experiments were independently repeated three times with similar results. The relative protein levels in (B) were normalized by GAPDH. Data are shown as mean ± SD, two-tailed Student’s t test.