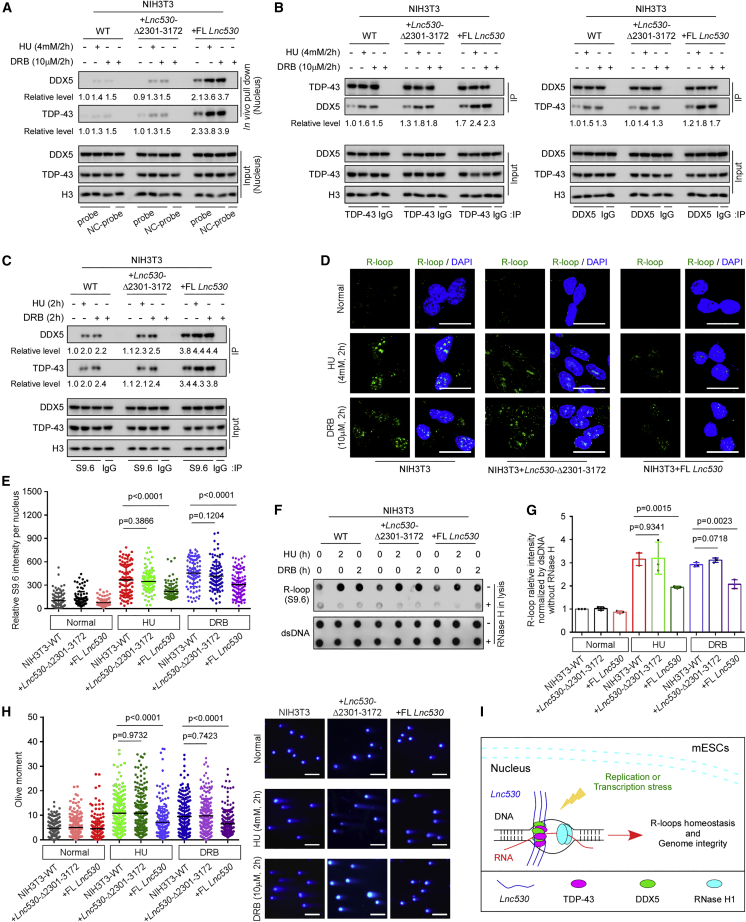
Figure 7.
Ectopic expression of Lnc530 in NIH3T3 cells decreases R-loop formation and increases genome stability
(A) In vivo RNA pull-down assay confirmed that under HU or DRB treatment conditions, TDP-43 and DDX5 interacted with FL Lnc530 but not Lnc530 Δ2,301–3,172 ectopically expressed in NIH3T3 cells. NC-probe, negative control probe.
(B) Reciprocal IP showed that ectopic expression of FL Lnc530, but not Lnc530 Δ2,301–3,172, increased TDP-43-DDX5 association in NIH3T3 cells. See also Figure S6.
(C) S9.6 IP showed that ectopic expression of FL Lnc530, but not Lnc530 Δ2,301–3,172, increased the accumulation of TDP-43 and DDX5 on R-loops in NIH3T3 cells.
(D and E) Immunostaining (D) and quantification (E) revealed that OE of FL Lnc530, but not Lnc530 Δ2,301–3,172, reduced the R-loop formation after HU or DRB treatment. At least 20 visual fields containing 500 cells were analyzed in three independent experiments. Scale bars, 20 μm.
(F and G) Dot-blot analysis (F) and quantification (G) confirmed that ectopic expression of FL Lnc530, but not Lnc530 Δ2,301–3,172, decreased the R-loop formation after HU or DRB treatment. dsDNA was used as internal reference.
(H) Neutral comet assay showed that forced expression of FL Lnc530, but not Lnc530 Δ2,301–3,172, alleviated DNA DSB formation after HU or DRB treatment. Left panel shows the quantification of comet tail length. Right panel shows representative images. At least 200 tails were analyzed in each group. Scale bar, 400 μm.
(I) Working model. LncRNA Lnc530 recruited more TDP-43 and DDX5 proteins to R-loops to efficiently prevent undesirable R-loop formation. All experiments were independently repeated three times with similar results. The relative protein levels in (A)–(C) were normalized by input. Data are shown as mean ± SD, two-tailed Student’s t test.