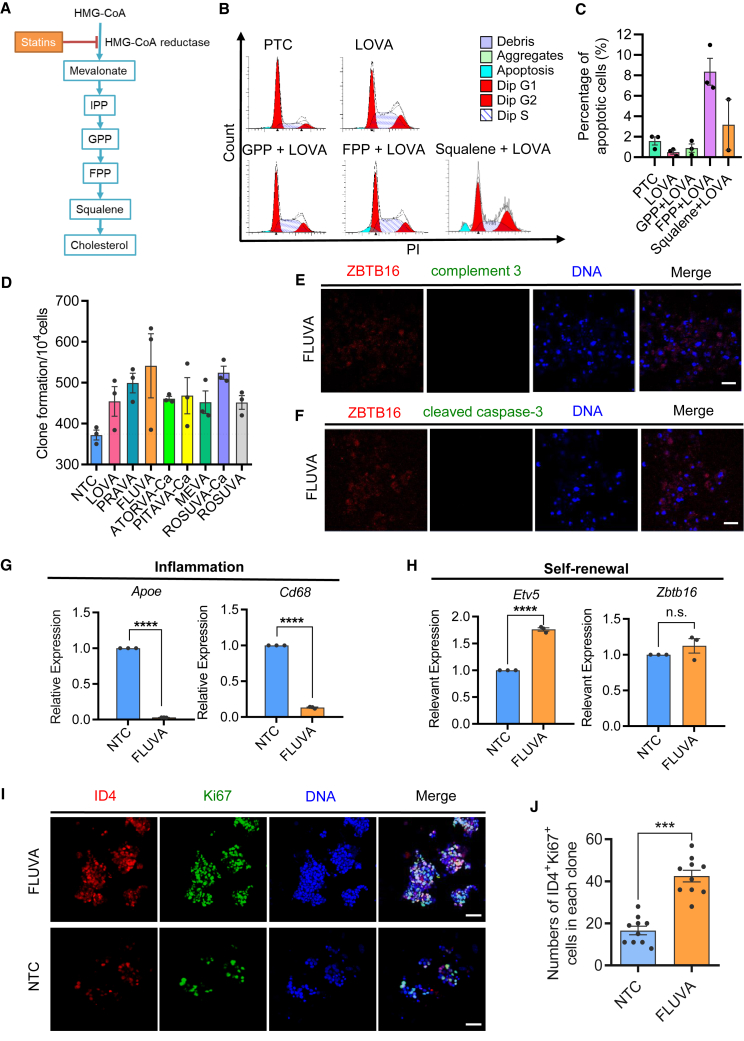
Figure 4.
Statins play an anti-apoptotic role by regulating the mevalonate pathway
(A) Schematic diagram of statin-dependent regulation of mevalonate metabolism.
(B) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis of cell apoptosis and cell-cycle distribution.
(C) Statistic histogram of apoptosis proportion for each treatment group. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.
(D) mSSC clone formation analysis after treatment with 8 kinds of statins. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.
(E and F) Immunofluorescent staining of undifferentiated spermatogonia marker (ZBTB16) and complement 3 (E) or cleaved caspase-3 (F) in mSSC clones cultured in the fluvastatin (FLUVA) group. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(G and H) qPCR analysis of the relative expression level of representative genes regarding inflammation (G) and self-renewal (H). Error bars indicate mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001, ns, non-significant.
(I) Immunofluorescent staining of ID4+ Ki67+ cells in mSSC clones cultured in NTC or FLUVA group. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(J) Statistic histogram of ID4 and Ki67 double-positive cells from FLUVA or NTC group from ten independent experiments. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001.