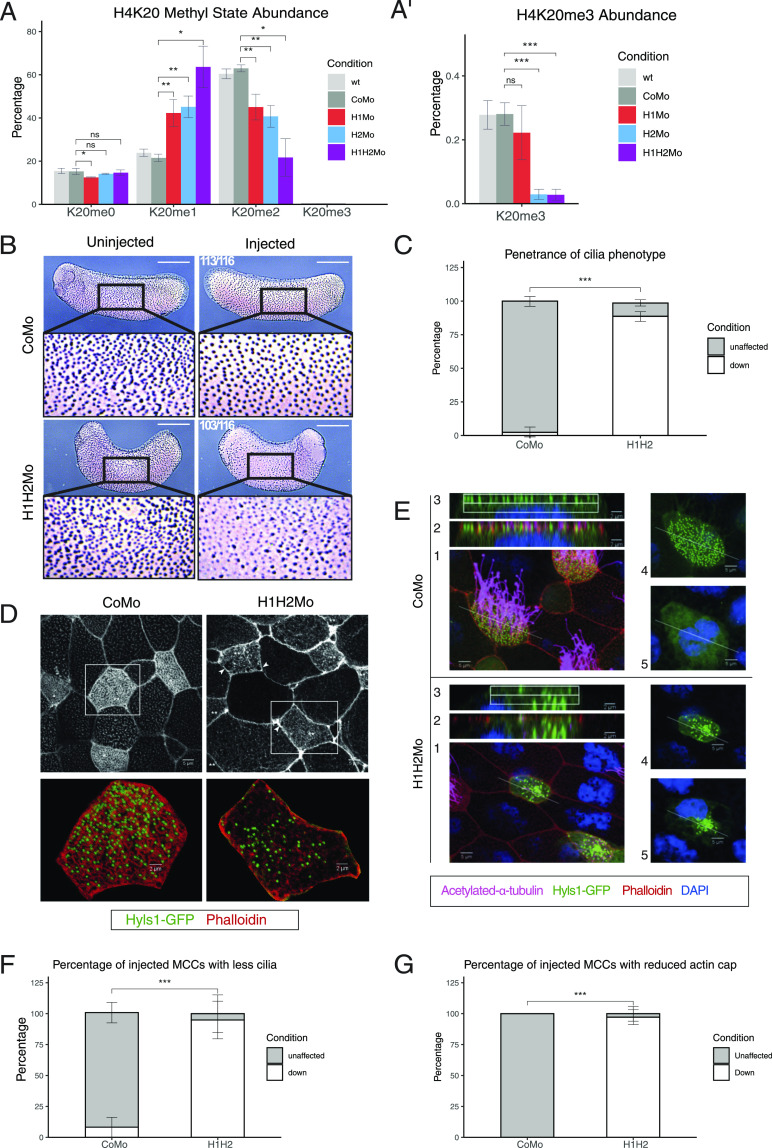
Figure 1. SUV4-20H1/H2 enzymes are required for ciliogenesis.
(A, A’) Relative abundance of H4K20 methyl states by mass spectrometry in X. laevis bulk embryonic chromatin upon control (CoMo), single or double KD of SUV4-20H1 and SUV4-20H2 enzymes. (B, C) Representative immunocytochemistry images of multiciliated cells (acetylated a-tubulin) in a tail bud stage embryo upon control or SUV4-20H dKD (inserts show enlarged sections of the same images, scale bars = 1 mm) and (C) quantification of (B) (n = 6 biological replicates). (D, E) Representative immunofluorescence images detailing the multiciliated cell phenotype upon suv4-20h1/2 KD. Basal bodies are green (hyls1-GFP), the cilia are magenta (acetylated a-tubulin antibody), the apical actin meshwork is red (phalloidin) and the nucleus is blue (DAPI). (E) Confocal analysis of the actin meshwork and docked basal bodies in CoMo or H1H2Mo-injected MCC. Panels show: 1—a representative MCC, 2—overlap between the actin cap and basal bodies on the apical surface, 3—basal bodies in only the uppermost Z-sections, 4—an apical view of the basal bodies, 5—a deep Z-section close to the cell nucleus. (F, G) Quantification of the number of MCCs showing reduced cilia and filamentous actin staining after confocal analysis. We measured 144 CoMo and 163 H1H2Mo-injected multiciliated cells. Error bars represent standard deviations.