FIGURE 3.
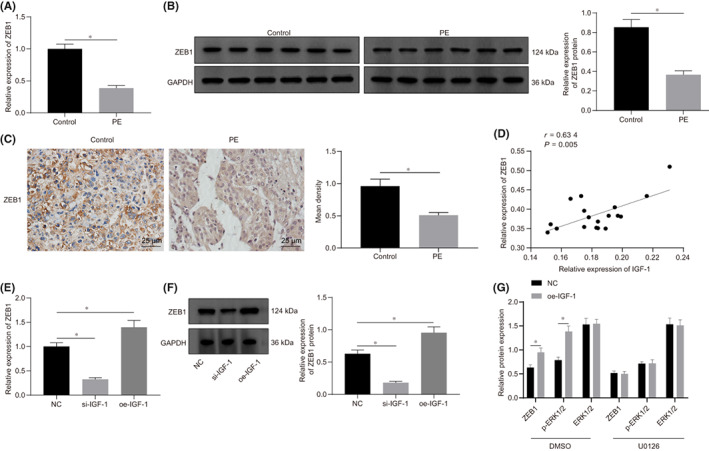
Expression of ZEB1 was elevated by IGF‐1 through the ERK/MAPK pathway. A, The RNA expression of ZEB1 in placental tissues of PE and NP detected by RT‐qPCR (n = 18). B, The protein expression of ZEB1 in placental tissues of PE and NP detected by Western blot analysis (n = 18), grey analysis was performed using Image J software. C, The expression of ZEB1 determined by IHC (n = 18) and the positive density was counted. D, ZEB1 was positively correlated with IGF‐1 expression (n = 18). E, The RNA expression of ZEB1 after HTR‐8/SVneo cells transfected with si‐IGF‐1 or oe‐IGF‐1 detected by RT‐qPCR. F, The protein expression of ZEB1 after HTR‐8/SVneo cells transfected with si‐IGF‐1 or oe‐IGF‐1 detected by Western blot analysis, the grey analysis was performed by Image J software. G, The expression of ZEB1, ERK1/2 and p‐ERK1/2 expression in the presence or absence of ERK/MAPK inhibitors in HTR‐8/SVneo cells transfected with oe‐IGF‐1 determined by Western blot analysis. All experiments were repeated three times. Data were measurement data and expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The independent sample t‐test was used for comparison between two groups. Comparisons among multiple groups were analysed by one‐way anova and followed by Tukey's post‐hoc test. * p < 0.05 vs. control group and NC group. The cell experiment was repeated three times. ZEB1, zinc finger E‐box binding homeobox 1; ERK1/2, extracellular signal‐regulated kinase 1/2; p‐ERK1/2, phosphorylated‐ERK1/2; NC, negative control
