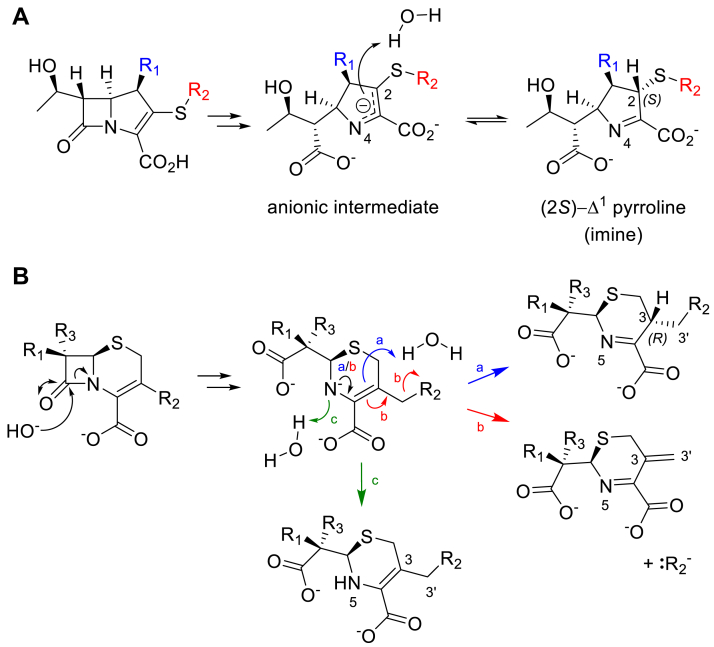
Figure 6.
Potential pathways for stereoselective protonation of carbapenems and cephems.A, possible pathway for (2S)-Δ1-imine formation in L1, via protonation of C-2 of an anionic intermediate by a non-activated water molecule. Note, the (2R)-Δ1-imine and Δ2-enamine tautomers (see Fig. 1C) are not observed crystallographically. B, cephem hydrolysis results in the formation of a common anionic intermediate (with negatively charged N-5) that reacts to give three possible products. Blue (a), tautomerization of the dihydrothiazine ring (black arrow) and diastereoselective protonation (3R) of C-3 by a water molecule. Red (b), dihydrothiazine tautomerization (black arrow) and loss of the C-3′ substituent (R2), resulting in an exocyclic methylene group. Green (c), N-5 protonation without tautomerization.