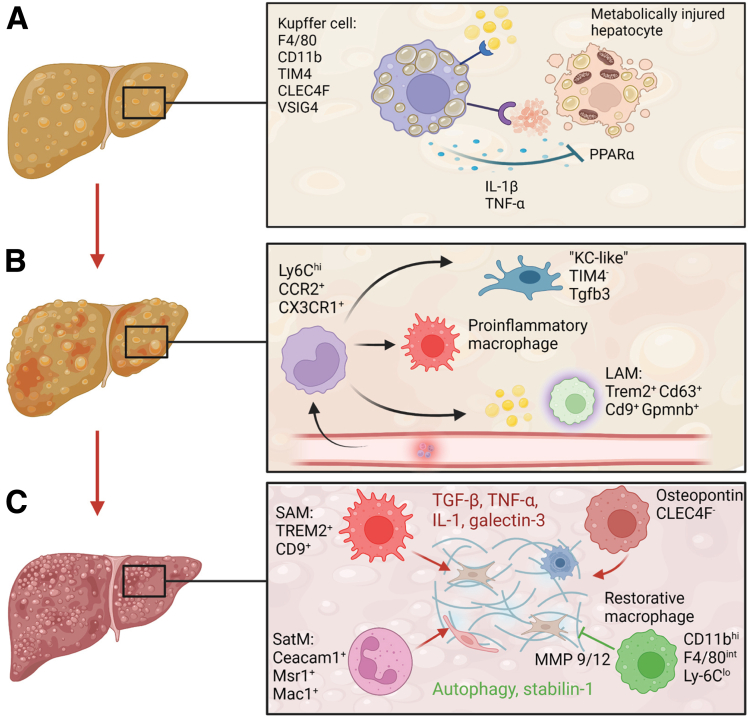
Figure 1.
Macrophages foster progression from nonalcoholic fatty liver to NASH and fibrosis. (A) Kupffer cells are activated upon ingestion of apoptotic fat-laden hepatocytes and free cholesterol, triggering proinflammatory activation. (B) The inflammatory microenvironment recruits monocytes that differentiate in heterogeneous monocyte-derived macrophage populations (Kupffer cell-like, inflammatory macrophages, and lipid-associated macrophages [LAMs]) based on signals from the environment. (C) Macrophage populations shape both profibrotic (red) and antifibrotic (green) processes within the fibrotic niche. Important phenotypic markers of the macrophage populations identified in mouse models are shown in the figure. CEACAM1, carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1; CLEC4F, C-Type Lectin Domain Family 4 Member F; Mac1, macrophage-1 antigen; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; Msr1, macrophage scavenger receptor 1; SAM, scar-associated macrophages; SatM, segregated-nucleus-containing atypical monocytes; Tgfb3, transforming growth factor β; VSIG4, V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 4. (Figure was created with BioRender).