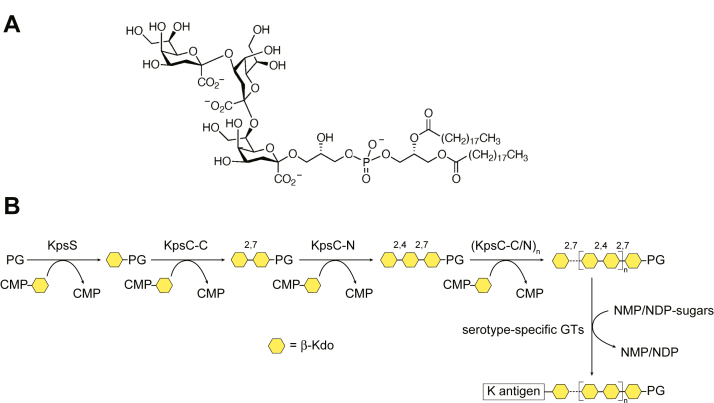
Figure 1.
Structure and biosynthesis of the KpsC reaction product.Panel A shows the structure of the phosphatidylglycerol-(Kdo)3 glycolipid intermediate synthesized by the combined actions of KpsS and the two GT modules in KpsC. The overall reaction scheme for the synthesis of an Escherichia coli group 2 capsular polysaccharide is depicted in Panel B, KpsS and KpsC are β-Kdo GTs, which transfer Kdo residues from CMP-β-Kdo donor to create a phosphatidylglycerol (PG)-based acceptor. KpsS adds the initial Kdo residue. This is followed by sequential addition of Kdo residues by the alternating actions of the KpsC-C and KpsC-N GT modules, to create a glycolipid acceptor containing 5 to 9 Kdo residues. The conserved KpsC reaction product is then elongated by a serotype-specific GTs to create a CPS belonging to a given K-antigen serotype. GT, glycosyltransferase.