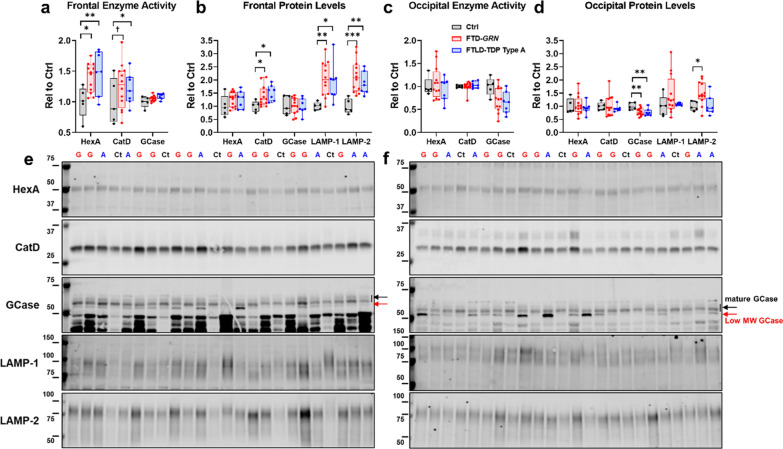
Fig. 1.
Increases in lysosomal enzyme activity and protein levels in frontal cortex of patients with FTD-GRN and sporadic FTLD-TDP type A. a Analysis of lysates from frontal cortex of patients with FTD-GRN or sporadic FTLD-TDP type A revealed similar increases in HexA activity (ANOVA, p = 0.0171) and CatD activity (ANOVA, p = 0.0404) in each patient group. No changes in GCase activity were detected (ANOVA, p = 0.4053). b Lysosomal protein levels followed a similar pattern, with both patient groups exhibiting increased levels of mature CatD (ANOVA, p = 0.0429), LAMP-1 (ANOVA, p = 0.0170), and LAMP-2 (ANOVA, p = 0.0019). c In contrast, no significant changes in enzyme activity were detected in occipital cortex, though there was a trend for reduced GCase activity in FTD patients (ANOVA, p = 0.0595). d Levels of mature GCase protein were reduced in occipital cortex of both patient groups (ANOVA, p = 0.0159) and the only elevated lysosomal protein in occipital cortex was LAMP-2, which was only elevated in patients with FTD-GRN (ANOVA, p = 0.0232). Immunoblots for frontal cortex are shown in e and for occipital cortex are shown in f. HexA = β-hexosaminidase A, CatD = cathepsin D, GCase = β-glucocerebrosidase. In e, f Ct = control, G = FTD-GRN, and A = sporadic FTLD-TDP type A. Molecular weight markers are identified by weight in kDa for each blot. †p < 0.1, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 by Fisher’s LSD post-hoc test. n = 5 controls, 12 patients with FTD-GRN, and 7 patients with sporadic FTLD-TDP type A