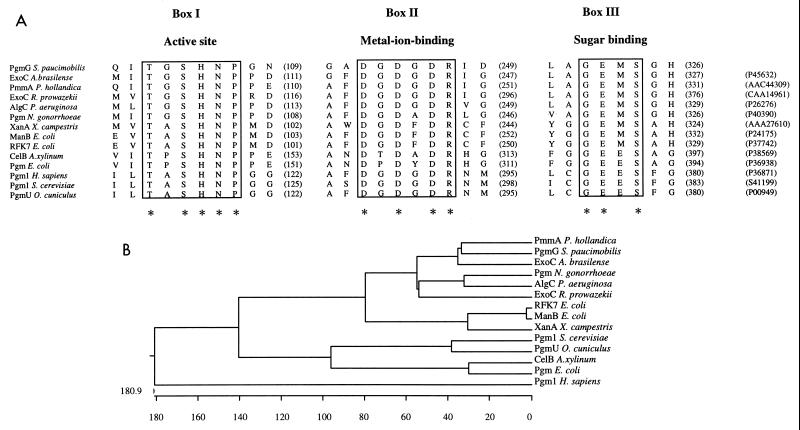
FIG. 1.
(A) Multiple amino acid alignment of the three characteristic consensus sequences present in 14 proteins with PGM and/or PMM activities from different organisms. Boxes I to III indicate the functional domains exhibiting highest similarity among the polypeptides. The amino acid sequences in boxes I, II, and III are known to be critical for PGM activity, based on the study of rabbit muscle PGM (10, 40). The box I motif contains the catalytic site of the enzyme; the box II motif contains a metal-ion-binding loop; and the box III motif interacts with the substrate. Asterisks below the sequences indicate residues conserved in all the enzymes. Numbers of intervening amino acids and accession numbers are given in parentheses. (B) Phylogenetic tree based on the multiple-sequence analysis of the fully sequenced PGM and PMM proteins. The CLUSTAL program (20) was used for the sequence alignment and the phylogenetic tree construction.