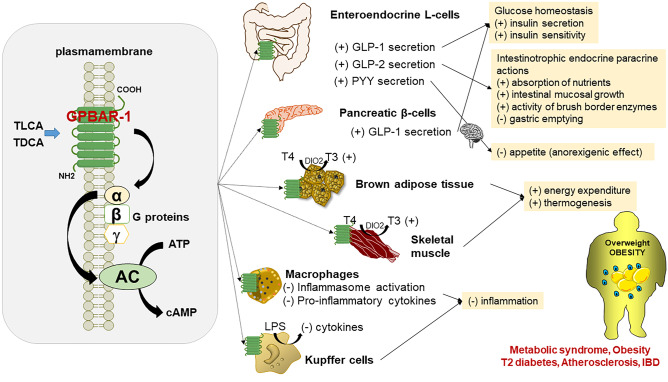
Fig. 8.
Systemic effects of bile acid (BA) as signalling molecules on the membrane-associated G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1 (GPBAR-1) in targets tissues. Binding of BA to GPBAR-1 activates the stimulatory G α protein which, in turn, triggers adenylate cyclase (AC) activation and cyclic AMP (cAMP) production. For the GPBAR-1, the rank order of potency of BA is TLCA > TDCA > TCDCA > TCA. Systemic effect following GPBAR-1 activation occur in the intestine via secretion of the incretin GLP-1, GLP-2, PYY. Additional effects are documented in the pancreas, brown adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, macrophages, and Kupffer cells (in the liver). The combination of GPBAR-1 stimulation likely prevent/modulate the expression of several metabolic abnormalities, including obesity. Of note, multiple pathways operate in this complex scenario which involve microbiome eubiosis/dysbiosis, BA type and pool profile, and distinct effects on GPBAR-1. Abbreviations: cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; DIO2, type II iodothyronine deiodinase; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; GLP-2, glucagon-like peptide 2; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PYY, peptide YY; T3, active thyroid hormone; T4, inactive thyroxine; TCA, taurocholic acid; TCDCA, taurochenodeoxycholic acid; TDCA, taurodeoxycholic acid; TLCA, taurolithocholic acid. (+) activation; (-) inhibition. After [117]