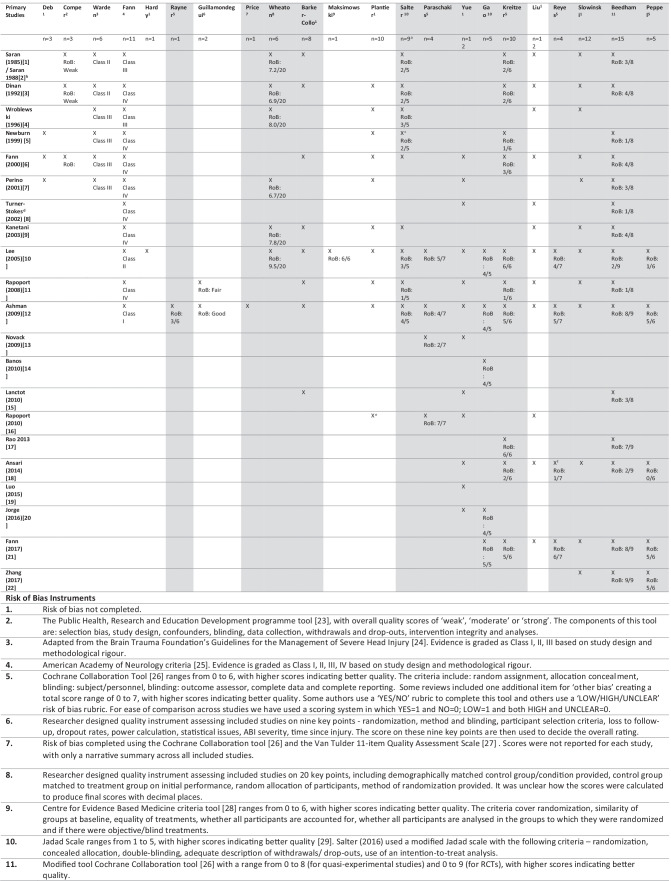
Table 2.
Citation Matrix Showing the Primary Studies within the 22 Included Systematic Reviews and Risk of Bias Assessment for each Primary Study
Columns in grey shading represent reviews with meta-analyses. Those columns with no shading are systematic reviews that provided a narrative synthesis only
The superscript numbers in the ‘systematic reviews’ row correspond to the risk of bias instrument used, which are listed with their corresponding number at the end of the table
Year of publication for the systematic reviews is not included due to space issues within the table. The systematic reviews have been ordered chronologically from left to right from oldest to most recently published
This table only includes primary studies from the systematic reviews that fulfilled our eligibility criteria
We only included classifications of evidence class if the classification system also included consideration of methodological rigour. Classifications of evidence class made only using study design (e.g. RCT as Class I), were not reported in this table as they do not include an assessment of methodological rigour (e.g. Plantier et al., 2016)
RCT randomised controlled trial, RoB risk of bias
aSalter et al. (2016) only completed methodological assessment for studies that included a comparison group
bThree independent authors (AH, FC & AJ) reviewed Saran (1985) and Saran (1988) and agreed these reports contain the same primary study
cSalter et al. (2016) did not include Newburn et al. (1999) in their meta-analysis due to insufficient data reported
dThe findings from Turner-Stokes et al. (2002) are not included for Yue et al. (2017) and Liu et al. (2019), as these reviews did not report the findings for the TBI sample separately
ePlantier et al. (2016) refers to this study as ‘Rapoport (1999)’. However, all extracted details in their manuscript and the citation in their reference list is for Rapoport (2010)
fReyes et al. (2019) refers to this study as ‘Ansari (2017)’. However, all extracted details in their manuscript and the citation in their reference list is for Ansari et al. (2014)