Fig. 1 |. The next-generation clinical care pathway for Alzheimer’s disease.
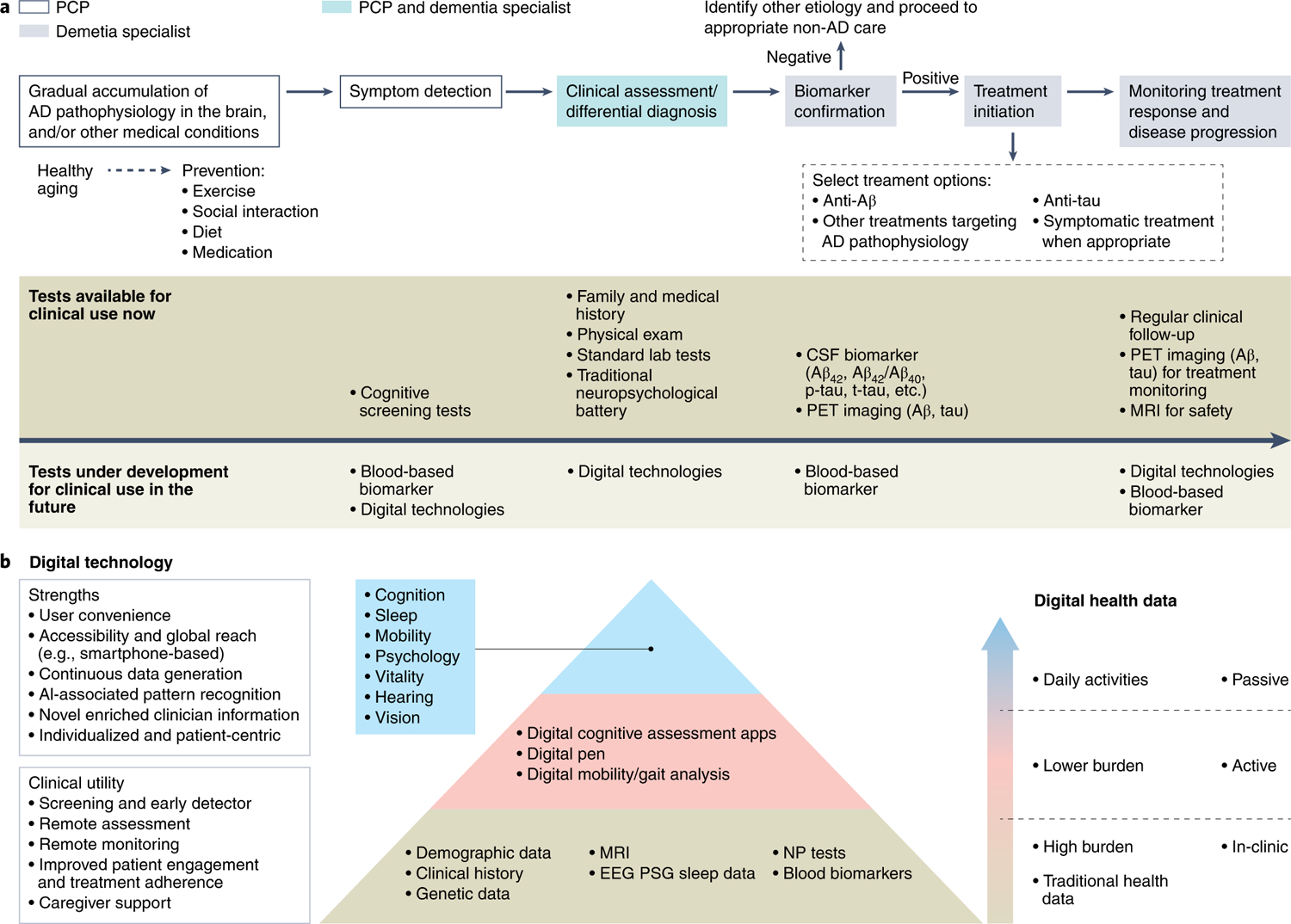
a, An overarching illustration. The next-generation clinical care pathway begins with healthy aging and participation in preventive lifestyle measures to slow or prevent accumulation of AD pathophysiology, with the goal of extending healthspan across populations. Symptom detection, triggered by concerned individuals or family members, or detected during a routine wellness visit, may involve cognitive testing and, in the future, blood-based biomarkers and digitally based assessments. This will be accompanied by clinical assessments involving standard laboratory tests and physical examination. Any recorded cognitive impairment will be confirmed with standardized biomarker tests. Individuals with confirmed disease will proceed to treatment initiation with relevant AD therapy followed by long-term monitoring, of which digital technologies and blood-based biomarkers will play a key role in the future. b, Digital health technologies in future AD clinical care and the path toward a precision monitoring and detection platform. A precision monitoring and detection platform will require a transformation from the traditional data collection methods to the inclusion of digital technologies. This will include active engagement technologies that require individual interaction and engagement to passive engagement technologies that collect data in the background while the individuals keep to their daily routine. AI, artificial intelligence; EEG, electroencephalogram; NP, neuropsychiatric; PSG, polysomnography.
