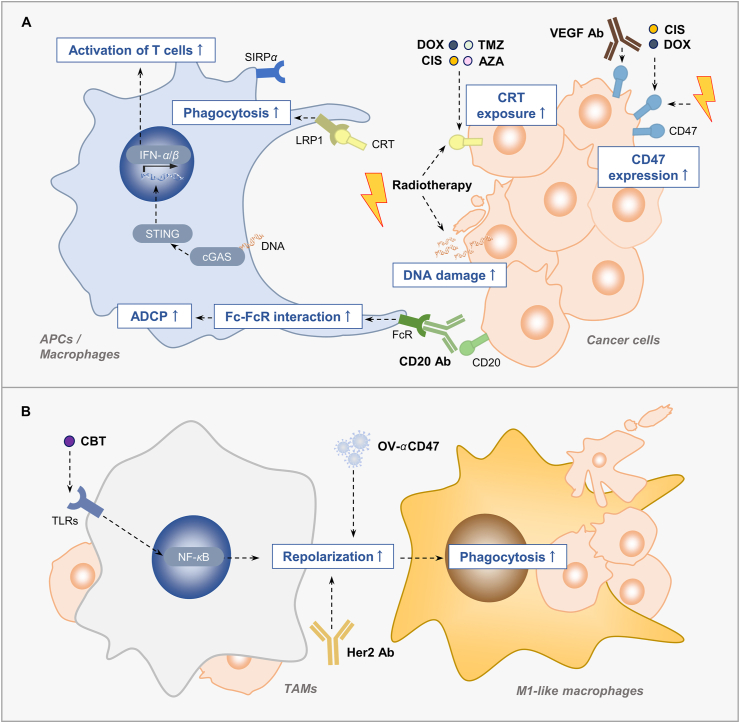
Figure 1.
Combination strategies enhance macrophage phagocytosis. (A) The combination treatment enhances phagocytosis by increasing the CRT on the cell surface, or enhancing Fc–FcR interaction. Chemotherapeutic drugs or radiotherapy enhance phagocytosis by increasing the surface expression of CRT. Some of them induces the ICD of cancer cells, cause more DNA damage, activate the cGAS–STING pathway of APC and finally leading to T cell activation. Anti-CD20 antibody augments ADCP through Fc–FcR interaction after combining with anti-CD47 antibody. Moreover, the up-regulation of CD47 on cancer cells by chemotherapy, radiotherapy or anti-VEGF antibody provides the opportunities to combine the agents targeting CD47. (B) Some combination strategies enhance macrophage phagocytosis by repolarizing the macrophage phenotype from TAMs to M1-like macrophage. CIS, cisplatin; TMZ, temozolomide; AZA, azacytidine; DOX, doxorubicin; CD20 Ab, anti-CD20 antibody; HER2 Ab, anti-HER2 antibody, CBT, cabazitaxel; OV-αCD47, the oncolytic virus expressing an anti-CD47 antibody.