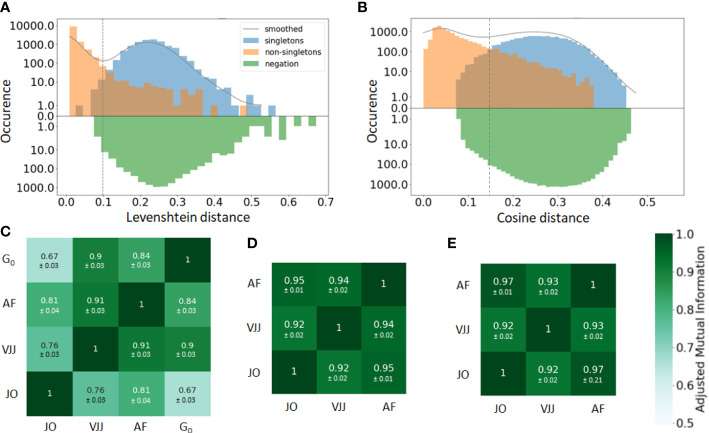
Figure 2.
(A, B) Distance to the nearest neighbor sequence distribution, both within the same repertoire (blue and orange) and to the negation sequences (green). The distances to nearest neighbors are labeled according to the ground truth (singleton or non-singletons), i.e. the clonal groups in the simulated data. Results are shown for both the (A) alignment-based method, i.e. based on common V-J segments and junction similarity, and (B) alignment-free method, based on the cosine distance between k-mers frequency vectors of each BCR (in the plot, k=7). The choice between alignment-based and alignment-free methods results in clearly different distributions of pairwise distances. The distance threshold used to define separate clusters is displayed for each clonal identification method (dashed vertical line). (C–E) Adjusted mutual information comparing the clustering partitions obtained from the three methods: Junction-only (JO), VJ & Junction (VJJ), Alignment-free (AF) and Ground-truth ( ). Results are averaged over all samples and provided for the (C) simulated, (D) germinal center, and (E) hepatitis B dataset. Each cell shows the average adjusted mutual information and the standard deviation. The ground truth of clonal assignment is only available for the simulated dataset (Subplot C).