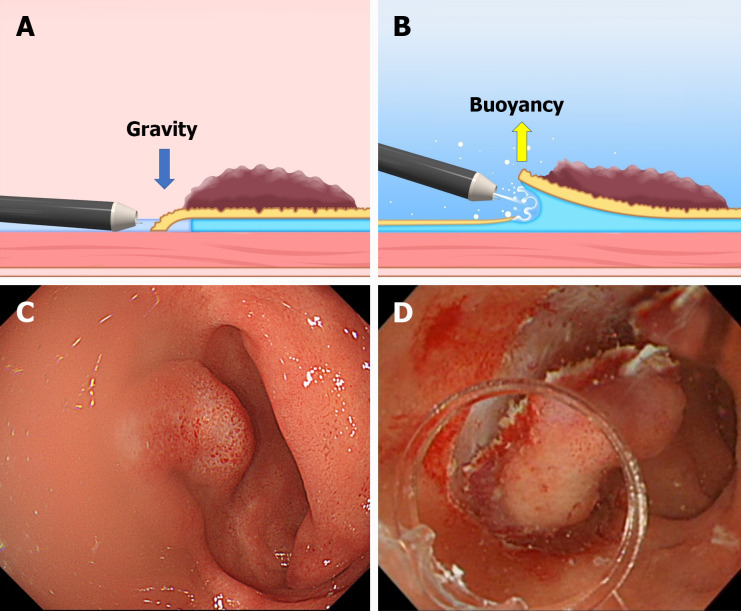
Figure 5.
The difference between the conventional endoscopic submucosal dissection and the underwater endoscopic submucosal dissection. A and C: The conventional endoscopic submucosal dissection for the lesion is located at the gravitational lower side. Gravity obstructs the opening of the mucosal flap. Incomplete submersion deteriorates the visual field; B and D: The underwater condition aids the opening of the mucosal flap by buoyancy. Water pressure from the endoscope (using its water supply function) also assists in opening the mucosal flap. Complete submersion improves the visual field. Citation: Figure 5A and B reprinted from Mitsuru Nagata. Advances in traction methods for endoscopic submucosal dissection: What is the best traction method and traction direction? World Journal of Gastroenterology 2022; 28: 1–22. Copyright ©Mitsuru Nagata 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc[8]. Figure 5C and D reprinted from Mitsuru Nagata. Underwater endoscopic submucosal dissection in saline solution using a bent-type knife for duodenal tumor. VideoGIE 2018; 3: 375–377. Copyright ©2018 American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Published by Elsevier Inc[20].