Figure 6.
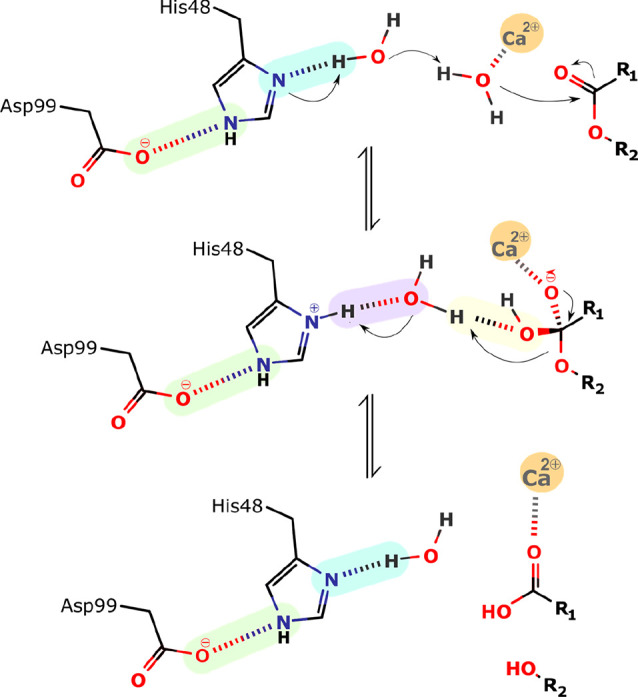
Schematic representation of the assisted-water mechanism proposed by Yu et al.45 Step 1: His48, which acts as a general base catalyst, abstracts a proton from the second water, which deprotonates the calcium-bound water molecule. This leads to the nucleophilic attack by the calcium-bound water on the carbonyl carbon of the substrate and the formation of the tetrahedral intermediate. Step 2: The departing alcoholate leaving group is protonated by the second water, which is itself protonated by His 48. Step 3: Collapses and the products are released.
