FIG 1.
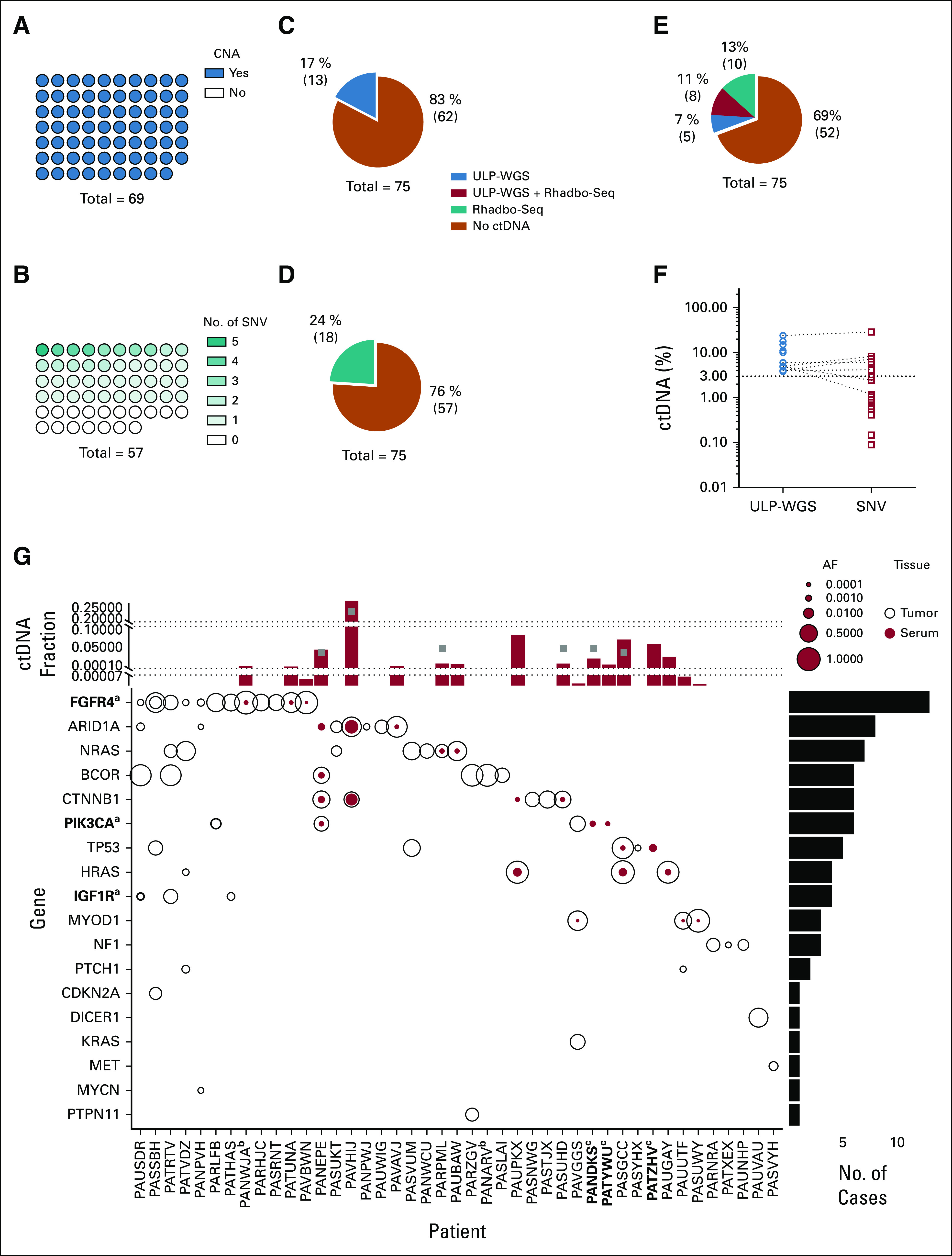
Characterization of FN-RMS genomics and ctDNA detection and quantification. (A) CNAs were identified in all 69 tumor samples by ULP-WGS. (B) SNVs were identified by the Rhabdo-Seq panel in 40 of 57 tumor samples with adequate sequencing coverage. ctDNA was detected in the serum in (C) 17% of the patients by ULP-WGS and (D) 24% of the patients by SNV identification with Rhabdo-Seq. (E) In total, 31% of patients had detectable ctDNA using a combination of ULP-WGS for CNA detection and Rhabdo-Seq panel for SNV detection. (F) Plotted are the percent ctDNA values for FN-RMS samples with detectable ctDNA by ULP-WGS (blue circles) and by Rhabdo-Seq (red circles). ctDNA content estimates are similar in cases where ctDNA is detected by both methods. However, the lack of SNVs in some cases results in ctDNA being unmeasurable by Rhabdo-Seq. In other cases, the lower limit of detection in Rhabdo-Seq allows for identification of very low content of ctDNA in some samples. (G) The plot depicts SNVs in genes (y-axis) targeted by the Rhabdo-Seq panel in patients with FN-RMS (x-axis) who have at least one variant found in either a tumor or serum sample. Open black circles represent variants found in the tumor, and solid red circles represent variants in serum. Circle size reflects allelic fraction of the identified variant. The histogram on top depicts ctDNA levels in serum samples from the patient (indicated on the x-axis) by ULP-WGS (gray squares) or SNV allelic fraction (red bar). When there are two SNVs, only the highest allelic fraction is represented by the red bar. The histogram is partitioned into three sections to help visualize values in cases with very low content of ctDNA. The histogram to the right represents the number of variants identified in the cohort. aGenes in bold indicate that a case had evidence of two mutations in that gene (FGFR4 in PASSBH, PIK3CA in PARLFB, and IGF1R in PAUSDR). bPatient IDs that are in bold indicate cases without available tumor data. cPatient IDs indicate cases without available germline DNA. The five cases with SNVs detected in the serum and not the tumor (PANEPE, PAUPKX, PANDKS, PATYWU, and PATZHV) were analyzed with a patient-matched normal DNA sample. AF, allelic fraction; CNA, copy number alteration; ctDNA, circulating tumor DNA; FN-RMS, fusion-negative rhabdomyosarcoma; SNV, single-nucleotide variant; ULP-WGS, ultralow passage whole-genome sequencing.
