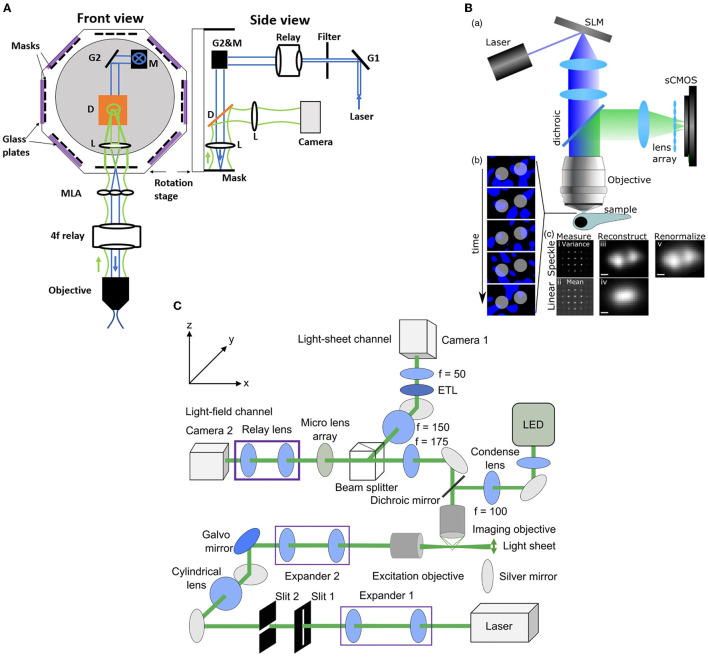
Figure 5.
Hybrid LFM systems. (A) Confocal LFM (Zhang et al., 2021a), front and side views. G: scanning galvo mirror; Relay: achromatic relay lens system; M: mirror; D: dichroic mirror; L: achromatic lens. The mask is placed on a rotational stage. (B) Structured light LFM (Taylor et al., 2018). Top, speckle-based LFM utilizes controlled speckle illumination by imaging an SLM pattern with a random phase mask onto the objective back focal plane. Bottom left, fluorescent beads are illuminated with random speckle patterns displayed into the SLM and the resulting light is recorded. Bottom right, comparison of the speckle, top, and linear, bottom, LFM by taking the variance and the mean of the recorded data. The middle picture shows the differences in the PSF measurements. The beads are resolved in the speckle LFM while unresolved in the linear LFM. Scale bar 2 μm (C) Light-sheet LFM (Wang et al., 2019): Simultaneous imaging by light-sheet and light-field modalities. On the right, a zoomed-in view of the detection paths is shown. (B) reproduced with permission from Taylor et al. (2018), (C) reproduced with permission from Wang et al. (2019) ©The Optical Society.