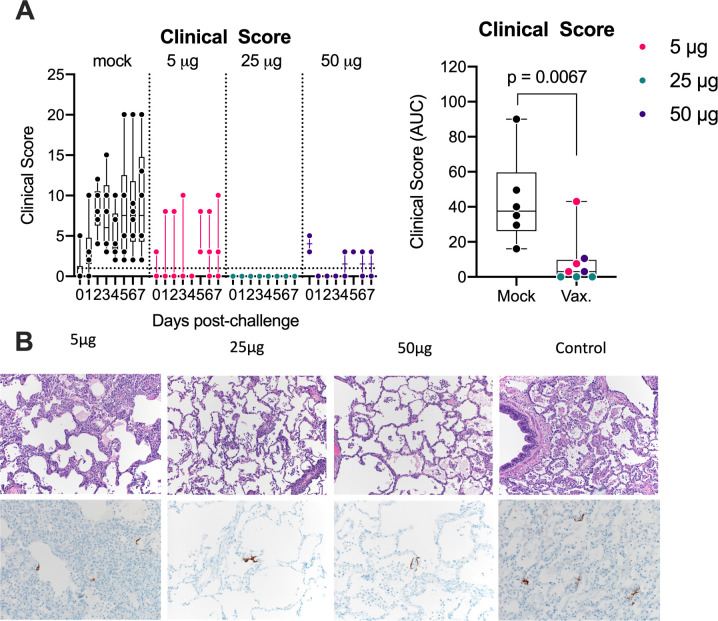
Fig 3. RepRNA-CoV2S vaccination reduces clinical disease and lung pathology.
(A) Animals were comprehensively evaluated for clinical disease including activity levels, appetite, appearance, and evidence of respiratory distress. Cumulative scores are shown. Area under the curve (AUC) of clinical scores were calculated 1–7 days after infection as described in the methods. Box and Whisker plots with minimum to maximum ranges are shown. Unpaired T-test p-values are shown, with p-values ≤ 0.05 considered significant. (B) Formalin fixed lung tissue was sectioned and stained with H&E (top panels) for SARS-CoV-2 antigen (bottom panels) at day 7 post-challenge. All six of the monkeys in the sham vaccinated group developed some degree of pulmonary pathology when inoculated with SARS-CoV-2, predominantly in the lower lung lobes. Pathological analysis of lungs in the vaccinated animals was generally less severe than in the control animals and lesions in the 25μg were less severe overall than compared to the 5μg or 50μg groups. Rare immunoreactivity to SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid was seen in vaccinated groups. Representative images are shown and the complete histological findings are provided in S3 Table.