Figure 1.
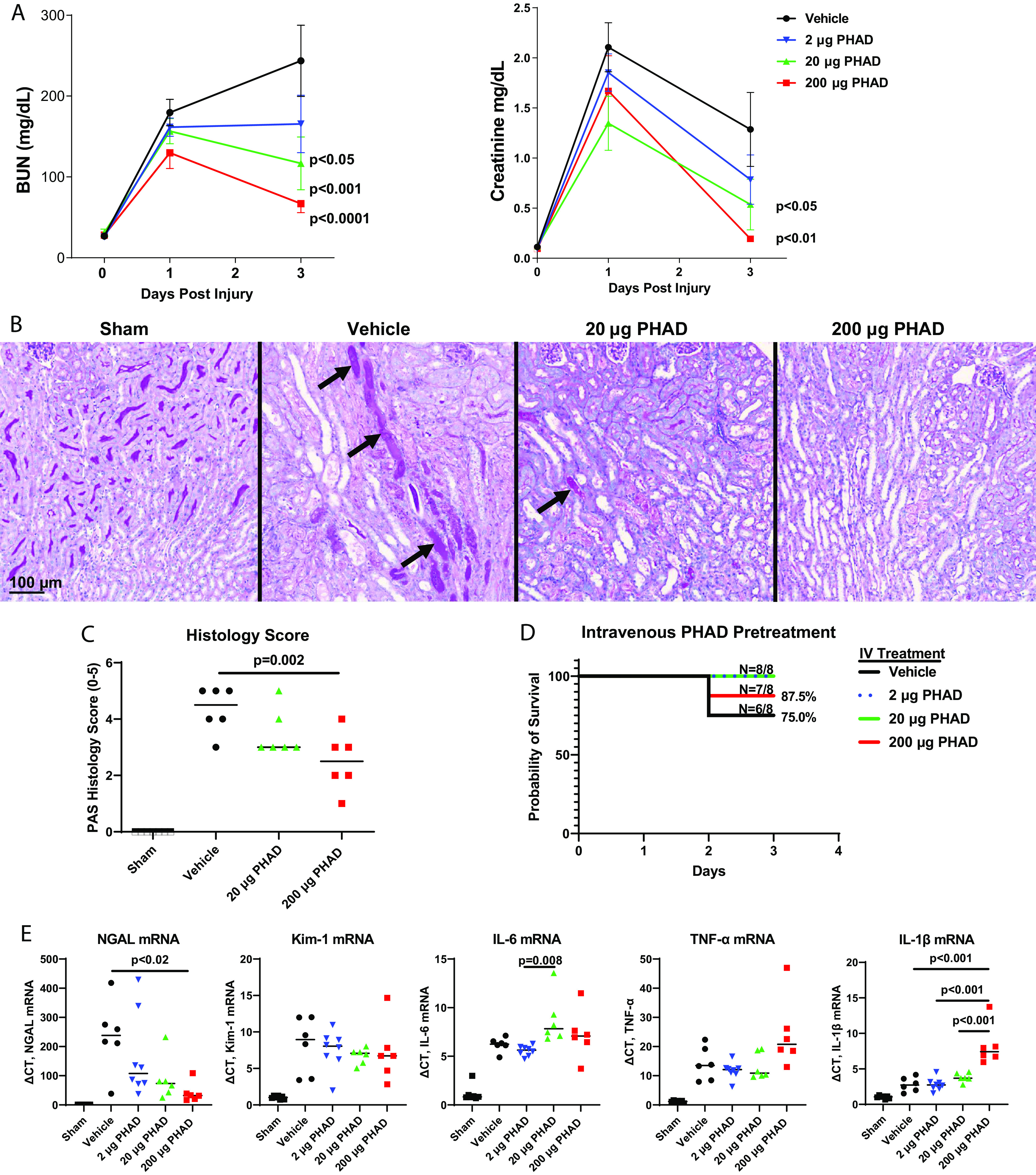
Pretreatment with 3-deacyl 6-acyl phosphorylated hexaacyl disaccharide (PHAD) in mice that underwent unilateral ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced acute kidney injury. Mice were pretreated with intravenous (IV) PHAD at 2, 20, and 200 µg/mouse or vehicle control 48 and 24 h prior to undergoing right nephrectomy followed by clamping of the left renal pedicle for 28 min. A: blood was analyzed for blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine at baseline (day 0) and postinjury days 1 and 3. Results are expressed as means ± SE with n = 8. Two-way ANOVA was used to compare differences between PHAD- and vehicle-treated mice over time, with P values indicated. B: representative images of periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-stained sections of the outer medulla day 3 after injury in sham, vehicle-treated, and PHAD-treated mice. Arrows point to casts within the collecting tubules. Scale bar = 100 µm. C: median tubular injury scores in the outer stripe of the outer medulla from PAS-stained sections day 3 after injury in sham, vehicle-treated, and PHAD-treated mice. D: 3-day survival curves. Group differences were compared by a log-rank test (P > 0.05). E: median quantitative RT-PCR for renal expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (Ngal), kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (Tnf-α), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) mRNAs. GAPDH was used as the internal control for quantitative RT-PCR, and change in threshold cycle (ΔCt) values is graphed relative to the sham group. For C and D, individual data points and medians are shown and between-group differences were compared by one-way ANOVA using Dunnett’s post hoc correction for multiple between-group comparison Kruskal–Wallis test, with significant P values (<0.05) indicated. n = 6.
