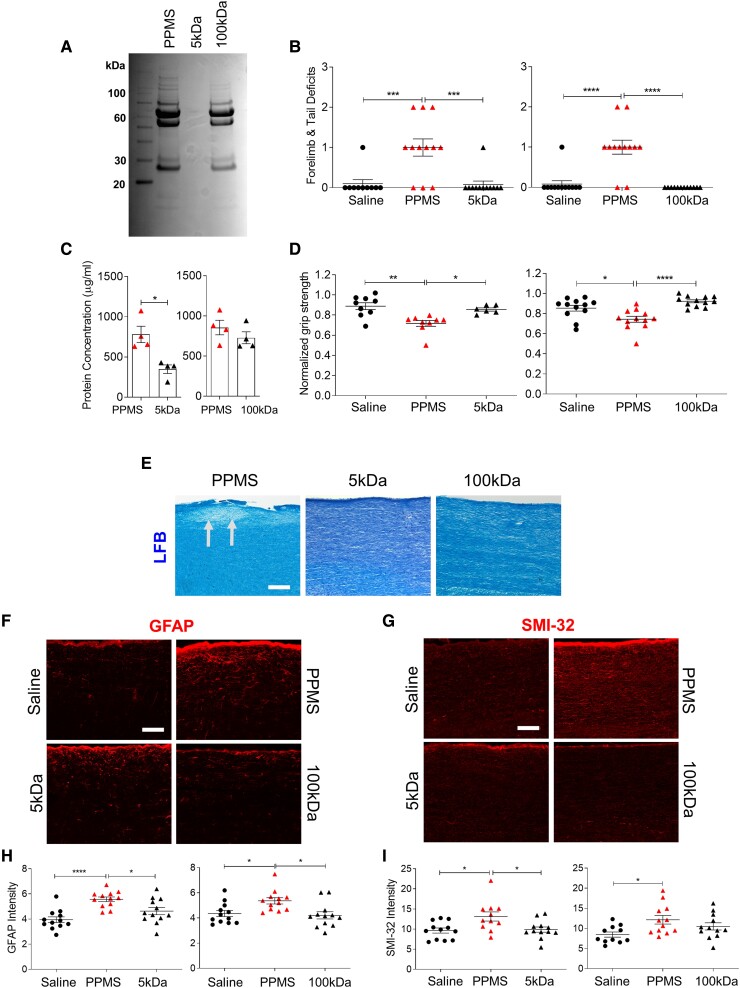
Figure 4.
Filtration of PPMS CSF attenuates its pathogenic capacity. (A) Representative Coomassie Blue staining of an unfiltered PPMS CSF sample (PPMS), 5 kDa-filtered PPMS CSF (5 kDa) and 100 kDa-filtered PPMS CSF (100 kDa). Individual PPMS CSF samples were filtered through 5 kDa (n = 4) or 100 kDa (n = 4) MWCO hollow-fibre tangential flow filters (Supplementary Table 2). (B) Motor deficit scores at 1 DPI. Saline (n = 15 mice), PPMS CSF (n = 18 mice), 5 kDa-filtered PPMS CSF (n = 12 mice), 100 kDa-filtered PPMS CSF (n = 12 mice). (C) Total CSF protein concentration of unfiltered PPMS CSF and PPMS CSF passed through a 5 kDa hollow fibre tangential flow filter (n = 4) or 100 kDa filter (n = 4) for three filtration cycles. (D) Forelimb grip strength force at 1 DPI normalized to pre-surgery baseline force. (E) Representative images of LFB staining in the cervical spinal cord dorsal column at 1 DPI. Arrows indicate demyelination. (F and G) Representative images of GFAP immunostaining (F) and SMI-32 immunostaining (G) in the cervical spinal cord dorsal column at 1 DPI. (H) Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity of GFAP+ astrocytes in the dorsal column. (I) Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity of SMI-32+ axons in the dorsal column. Data plotted as mean ± SEM. Each point represents an individual CSF sample (C) or mouse (B, D, H and I). Paired Student’s two-tailed t-test (C). One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s test (B, D, H and I). ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. Scale bars = 100 µm.