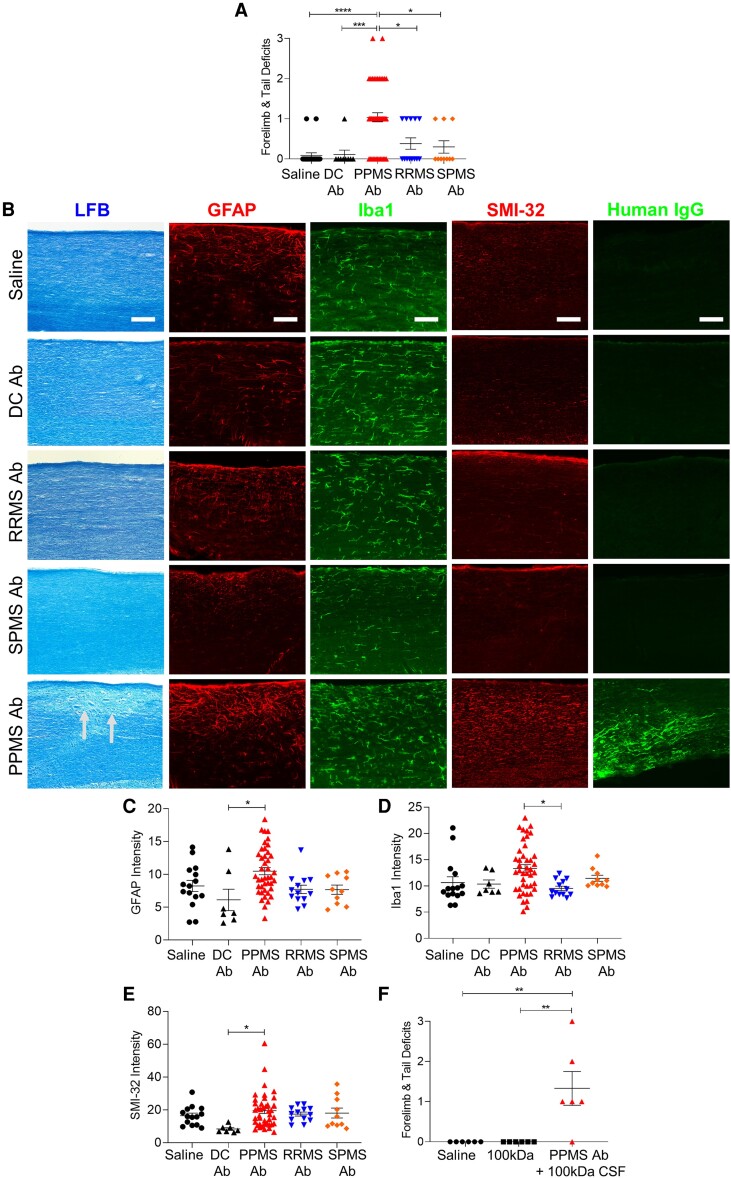
Figure 6.
Pathogenic rAbs derived from B lymphocytes in PPMS CSF induce motor deficits and spinal cord pathology. (A) Motor deficit scores at 1 day post intrathecal delivery of rAbs derived from MS patients: PPMS (n = 7), RRMS (n = 4), SPMS (n = 4), and disease controls (DC): HTLV-1 (n = 1) and ALS (n = 2) (Table 2). Saline (n = 22 mice), DC rAbs (n = 9 mice), PPMS rAbs (n = 51 mice), RRMS rAbs (n = 13 mice), SPMS rAbs (n = 10 mice). (B) Representative images of cervical spinal cords stained with LFB, GFAP, Iba1, SMI-32, or human IgG at 1 DPI. Arrows indicate demyelination. Scale bars = 100 µm. (C) Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity of GFAP+ astrocytes in the dorsal column. (D) Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity of Iba1+ microglia in the dorsal column. (E) Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity of SMI-32+ axons in the dorsal column. (F) Motor deficit scores of mice injected with saline (n = 6 mice), 100 kDa-filtered PPMS CSF (n = 6 mice) or PPMS rAbs added to 100 kDa-filtered PPMS CSF from the same patient (n = 2 PPMS patients, n = 6 mice) at 1 DPI. Data plotted as mean ± SEM. Each point represents an individual mouse. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s test (A, C–F). ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.