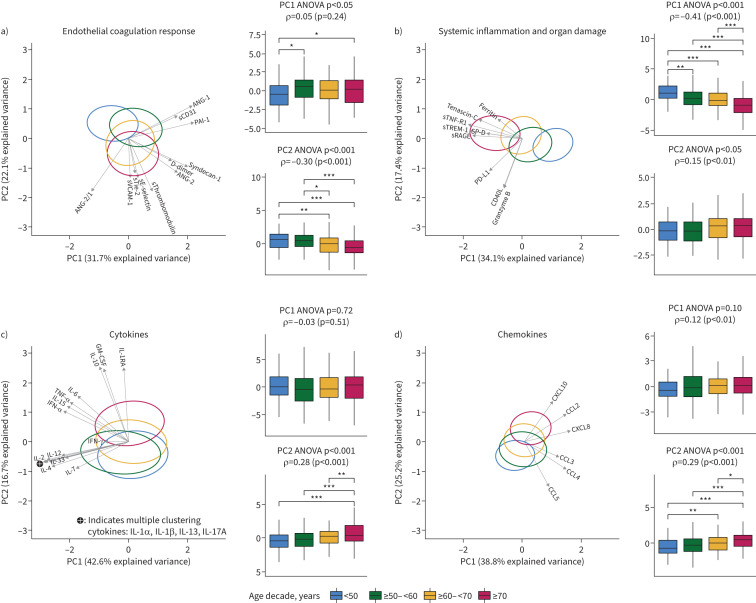
FIGURE 3.
Principal component analysis (PCA) of host response domain differences between age groups: a) endothelial and coagulation response, b) systemic inflammation and organ damage, c) cytokines and d) chemokines. Principal components (PCs) 1 and 2 are plotted per domain. For each domain, the x- and y-axes are labelled with the percentage of the total variance within that domain that is explained by PC1 and PC2, respectively. The complete contribution of each biomarker to a PC score is depicted in supplementary table S6. The ellipse indicates the central 10% of each age group, colour coded as indicated in the key at the bottom of the figure. The arrows indicate the direction (arrow orientation) and strength (arrow length) of the correlation between each biomarker and the PCs. Next to each PCA plot are box plots with 1.5 interquartile range whiskers of PC1 and PC2. Herein, upper p-values were obtained by ANOVA between age groups: ρ-values with accompanying p-values were generated using a Spearman's correlation with ageing on a continuous scale. Note that a negative association of a PC with ageing may still reflect a positive association with biomarker concentration, as reflected by the direction of the arrows. Post-hoc testing was done with a Tukey test. *: p<0.05; **: p<0.01; ***: p<0.001. ANG: angiopoietin; sTie-2: soluble Tie-2; sE-selectin: soluble E-selectin; sThrombomodulin: soluble thrombomodulin; sVCAM-1: soluble vascular cellular adhesion molecule 1; PAI-1: plasminogen activator inhibitor 1; sCD31: soluble cluster of differentiation 31; sRAGE: soluble receptor for advanced glycation end-products; sTNF-R1: soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor 1; sTREM-1: soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1; SP-D: surfactant protein D; CD40L: CD40 ligand; PD-L1: programmed death ligand 1; CCL:C-C motif chemokine ligand; CXCL: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; IL: interleukin; TNF: tumour necrosis factor; GM-CSF: granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN: interferon.