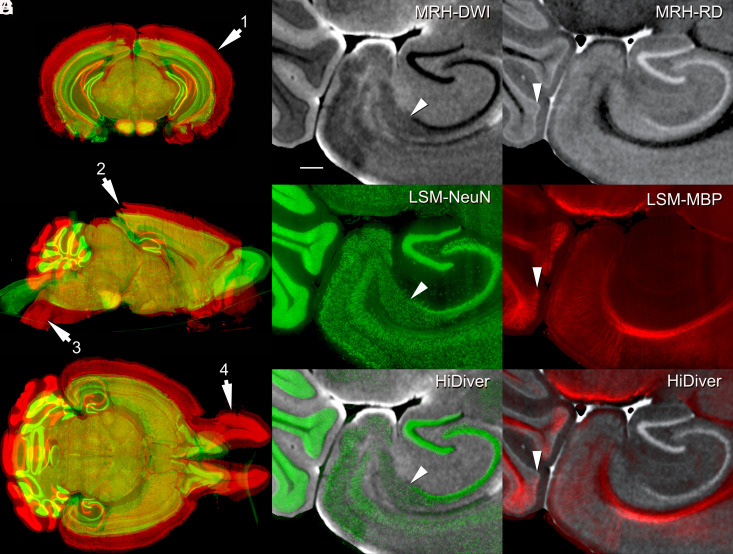
Fig. 3.
HiDiver integration of MRH and LSM. Distortion of LSM samples was corrected by registering to the MRH reference volume of the same specimen. Panel (A) flags four types of registration problems in the LSM data—before (red) and after (green) correction with specimen 200316-1:1. Arrow 1 highlights variable expansion during LSM processing that can range up to 100% for the olfactory bulbs, but averages about ~60% globally in this case. Arrow 2 flags tears in the visual cortex introduced during dissection. Arrow 3 marks an exaggerated flexure of the brainstem, while arrow 4 indicates spread of the olfactory bulbs. All the three LSM channels were brought into alignment with MRH by diffeomorphic registration. Panels (B–D) (specimen 191209-1:1) provide an overview of HiDiver alignment where (B) is DWI, (C) is NeuN, and (D) is the HiDiver product. The arrowheads in these overlays point to the CA1, subiculum boundary. (E–G) show the RD with MBP and a similar trio that points to a layer of Purkinje cells and Bergmann glia in the cerebellar cortex. The MBP label extends into and just above this layer. (Scale bar in B is 200 µm.)