Fig. 5.
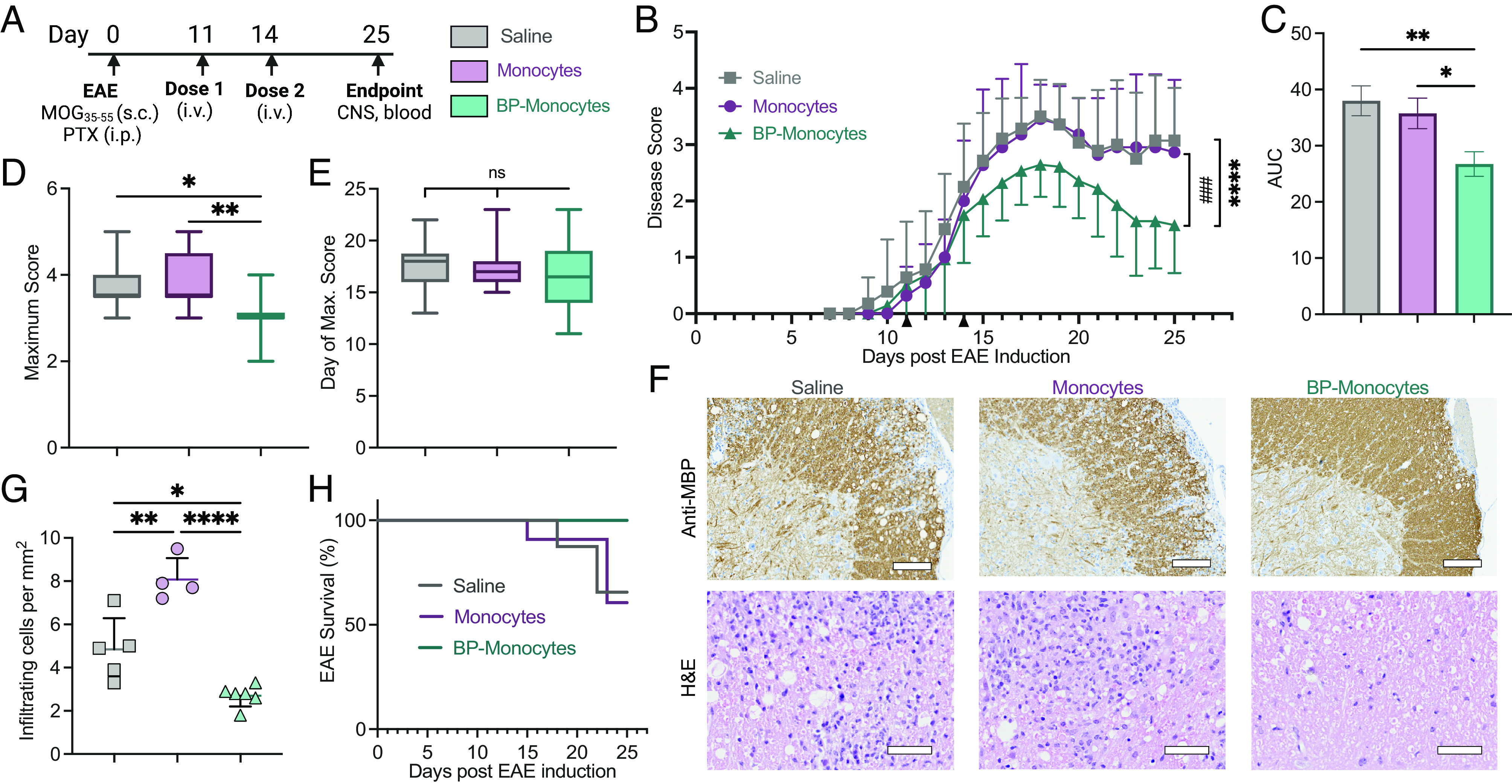
Backpack-monocytes are therapeutically effective. EAE was induced in female C57BL/6J mice. (A) The mice were treated with monocytes, backpack-laden monocytes (BP-monocytes), or saline on days 11 and 14 (i.v. tail vein). The mice were scored until day 25. (B) Disease score over time; mean ± SE (n = 11 to 14). (C) Area under the curve (AUC) of disease score; mean ± SD (n = 11 to 14). (D) Maximum disease score; mean ± SD (n = 11 to 14). (E) Day of onset of maximum score; mean ± SD (n = 11 to 14). (F) Representative antimyelin basic protein (MBP) staining, revealing areas of demyelination, and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, revealing inflammatory infiltrates, for lumbar spinal cord sections of mice from B (n = 5). Anti-MBP scale bar represents 100 µm. H&E scale bar represents 50 µm. (G) Inflammatory infiltrating cells per mm2 from lumbar spinal cord sections from F; mean ± SD (n = 4 to 6). (H) EAE survival percentage from mice in B. (n = 11 to 14). For B, data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison; ****P < 0.0001 comparing saline and backpack-monocytes; ###P < 0.001 comparing monocytes and backpack-monocytes. For C and E, data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD test; ns, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
