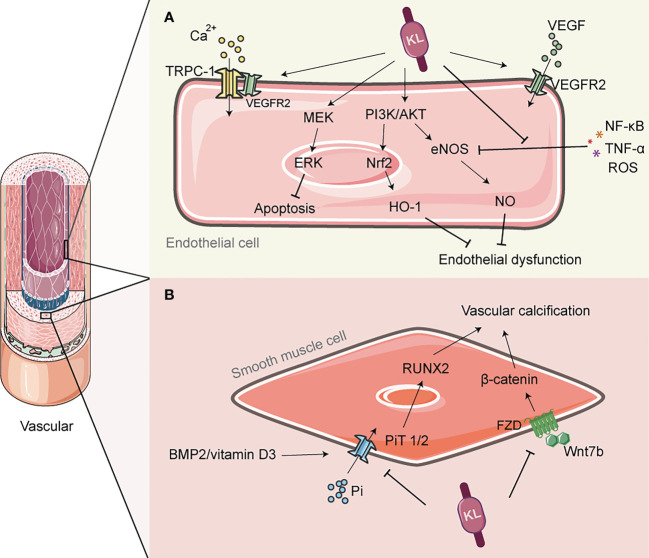
Figure 2.
The role of Klotho in vascular protection. (A) Klotho can activate PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 to enhance endothelial antioxidant defense; It can also activate PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway, and alleviate the inhibition of eNOS phosphorylation by inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, thereby promoting NO production and preventing endothelial cell dysfunction. Klotho is involved in the transmission of VEGF signaling and regulates Ca2+ influx, which helps to maintain endothelial integrity. (B) Klotho inhibits phosphate uptake by vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), leading to improved vascular calcification. It also inhibits the PiT2/RUNX2 signaling pathway, which improves extracellular matrix calcification. Additionally, Klotho inhibits the Wnt7b/β-catenin signaling pathway, which prevents VSMC calcification. NO, nitric oxide; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; Nrf2, Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; TRPC-1, transient-receptor potential canonical Ca(2+) channel 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; PiT, Pi transporter; RUNX2, runt-associated transcription factor 2.