Figure 7. Cortactin stabilizes Arp2/3‐mediated branches as well as SPIN90‐Arp2/3 at the pointed end of filaments.
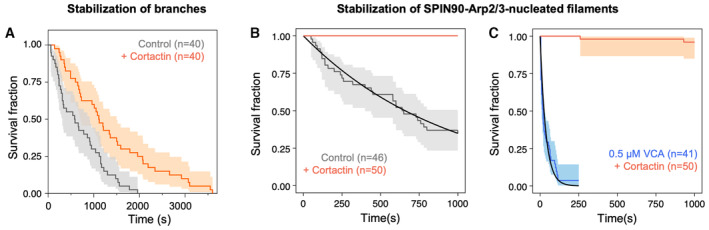
- The fraction of remaining branches, versus time, exposed to 0.16 μM G‐actin (black) supplemented with 50 nM cortactin (red). The branch junctions were exposed to an average force of 1.4 pN. Similar results were obtained with different forces and different protein concentrations (Appendix Fig S3).
- The fraction of remaining SPIN90‐Arp2/3‐nucleated filaments, versus time, exposed to 0.15 μM G‐actin (black) supplemented with 10 nM cortactin (red).
- The fraction of remaining SPIN90‐Arp2/3‐nucleated filaments, versus time, exposed to 0.15 μM G‐actin, with 0.5 μM VCA (black) supplemented with 10 nM cortactin (red).
Data information: Shaded areas represent 95% confidence intervals. Each curve is the result of a single experiment. Repeats of experiments in (A) with different forces and aging are shown in Appendix Fig S3. The experiments shown in (B, C) were repeated three times, yielding similar results.
Source data are available online for this figure.
