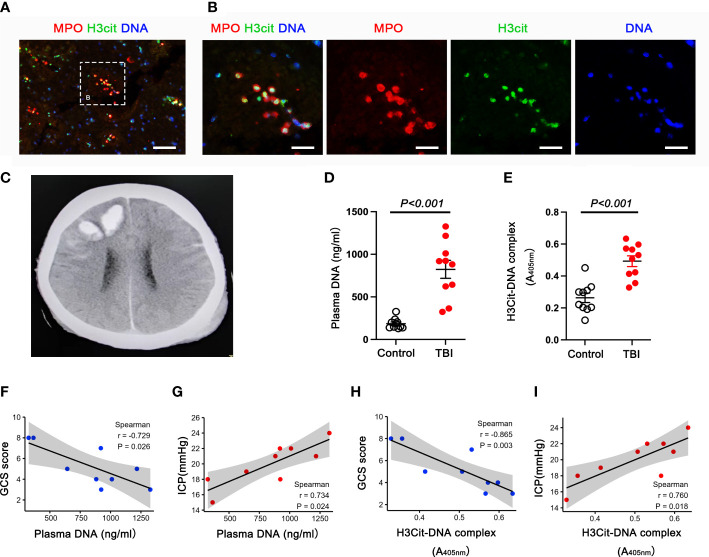
Figure 1.
NETs are found in the brain and circulating blood from TBI patients and have a significant correlation with GCS and ICP. (A, B) Representative immunofluorescence images (A) displaying the NET formation (H3Cit-positive neutrophils) in the brain tissue sections from TBI patients. Enlarged images on the right side (B). Scale bar = 50 μm (A); Scale bar = 200 μm (B). A representative CT image from a TBI patient (C). The image shows the right frontal contusion and hematoma. (D, E) Quantification of the Levels of plasma DNA (D), plasma H3Cit-DNA complex (E) in the peripheral blood from healthy donors (n = 10) and TBI patients (n = 10). (F-I) Correlation among the levels of plasma DNA, plasma H3Cit-DNA complex with Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) and intracranial pressure (ICP). Spearman correlation analysis was applied with r=-0.729, P =0.026 (F) (plasma DNA correlate with GCS score), r=0.734, P =0.024 (G) (plasma DNA correlate with ICP), r=-0.865, P =0.003 (H) (plasma H3Cit-DNA complex correlate with GCS score), r=0.734, P =0.024 (I) (plasma H3Cit-DNA complex correlate with ICP). The statistical graph shows that the higher the level of NETs, the greater the degree of TBI.