Fig. 2.
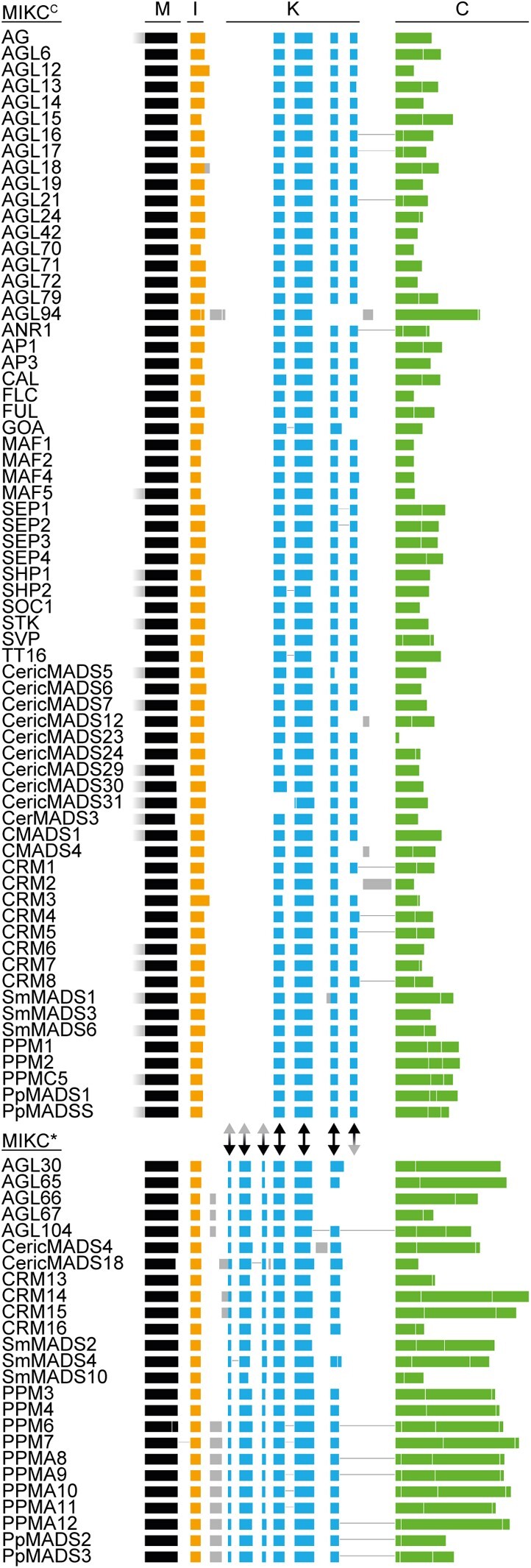
Exon homology of MIKCC- and MIKC*-type genes from Arabidopsis thaliana, Ceratopteris richardii, Selaginella moellendorffii, and Physcomitrium patens. Colored boxes represent coding exons of all MIKCC- and MIKC*-type genes from A. thaliana, C. richardii, S. moellendorffii, and P. patens. Introns and noncoding exons are not shown. Exons encoding for the MADS-domain, the intervening domain (I-domain), the keratin-like domain (K-domain), and the C-terminal domain (C-domain) are labeled on top and are additionally color coded in black, yellow, blue, and green, respectively. Exons with uncertain homology assignment are color-coded in gray. Exons encoding for MADS-, I-, and K-domain were aligned according their homology based on a multiple sequence alignment of the encoded proteins back translated into a codon alignment (for details, see Materials and Methods). Fused exons are connected by horizontal black lines. Two-headed arrows between MIKCC- and MIKC*-type genes illustrate presence (black) or absence (gray arrowhead) of homologous exons in either of the two subfamilies.
