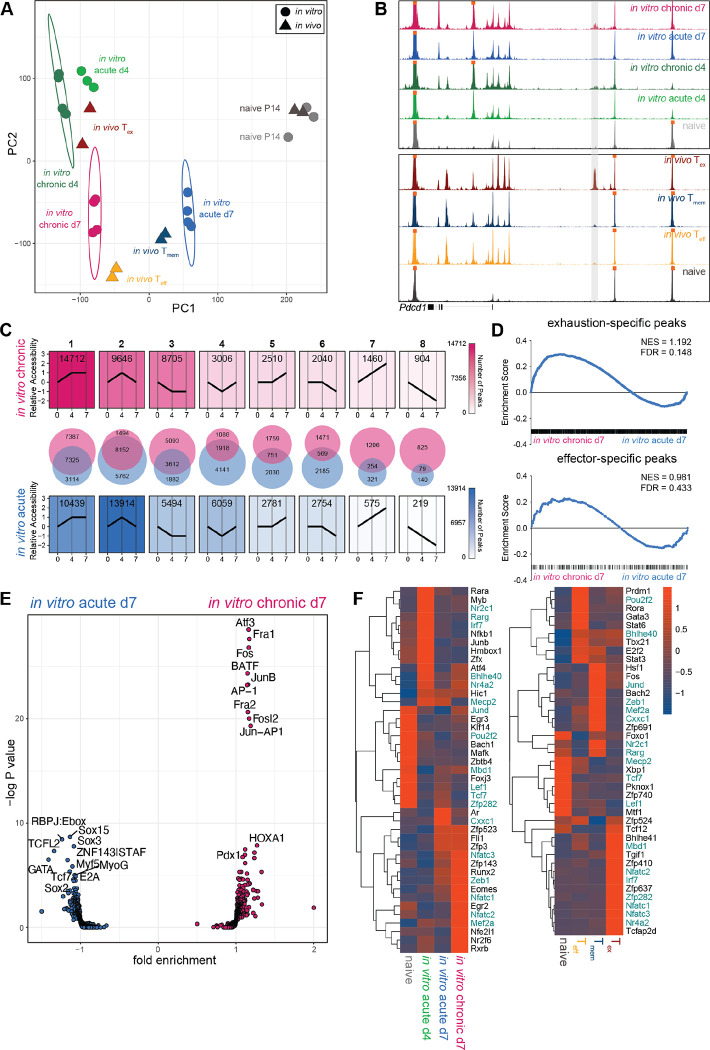
Fig. 3. In vitro chronically stimulated P14 cells develop epigenetic signatures of Teff and Tex.
(A) PCA of ATAC-seq data from in vitro chronically and acutely stimulated P14 cells and previously published in vivo CD8 T cell subsets (48). (B) ATAC-seq signal tracks for in vitro chronically and acutely stimulated P14 cells and previously published in vivo CD8 T cell subsets (48); −23.1kb enhancer of Pdcd1 locus highlighted in gray. (C) Trajectory analysis (see Methods) of chromatin accessibility patterns during in vitro chronic or acute stimulation. (D) Peak set enrichment analysis (PSEA) of Tex- and Teff-specific ACRs in in vitro chronically and acutely stimulated P14 cells. (E) Transcription factor (TF) motif accessibility in differential ACRs between in vitro chronically and acutely stimulated P14 cells. (F) Rank calculated via Taiji analysis in [left] in vitro chronically and acutely stimulated P14 cells and [right] previously published in vivo CD8 T cell subsets (37), filtered by mean>0.0001 and fold change>5. Heat scale indicates z-score of rank as calculated by PageRank algorithm. Colored text indicates shared TFs between in vitro and in vivo analyses.