Figure 2. Diagram showing different ways of targeting ferroptosis.
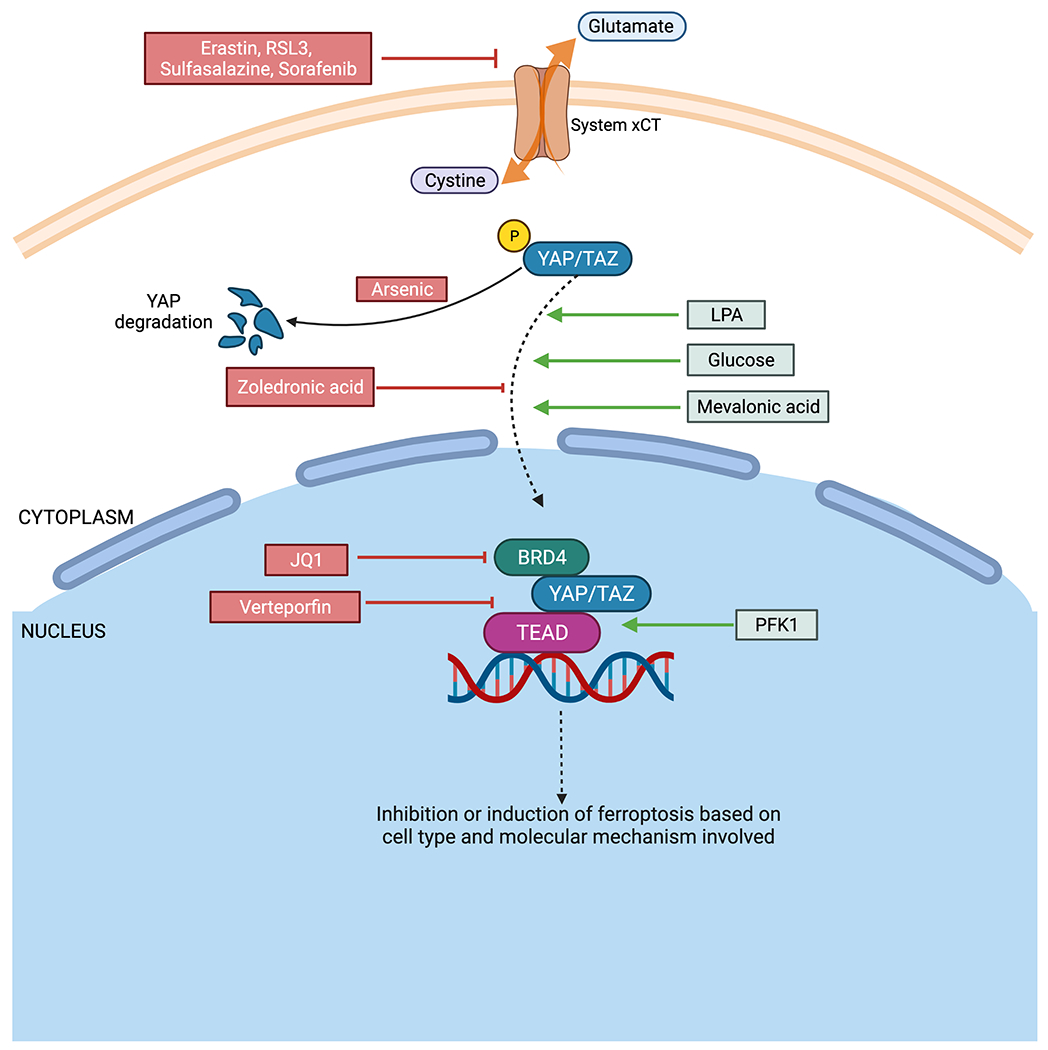
Drugs such as Erastin, RSL3, Sulfasalazine, Lanperisone and Sorafenib can inhibit system xCT and thereby induce ferroptosis. Arsenic treatment causes YAP ubiquitination and degradation.
Ferroptosis can be induced by activating YAP/TAZ. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and mevalonic acid aid in nuclear localization of YAP/TAZ while glucose stabilizes the activity of YAP/TAZ through inactivation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and the Hippo pathway. Phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK1) promotes YAP/TAZ binding with transcription factor, TEAD. Inhibition of YAP/TAZ can be mediated by maintaining dephosphorylated state using mevalonate pathway inhibitors such as zoledronic acid. Verteporfin inhibits interaction between YAP/TAZ with TEAD, thereby preventing binding with DNA for transcription. JQ1 inhibits BRD4, which forms a part of the YAP/TAZ-TEAD complex.
Images constructed with Biorender.
