Abstract
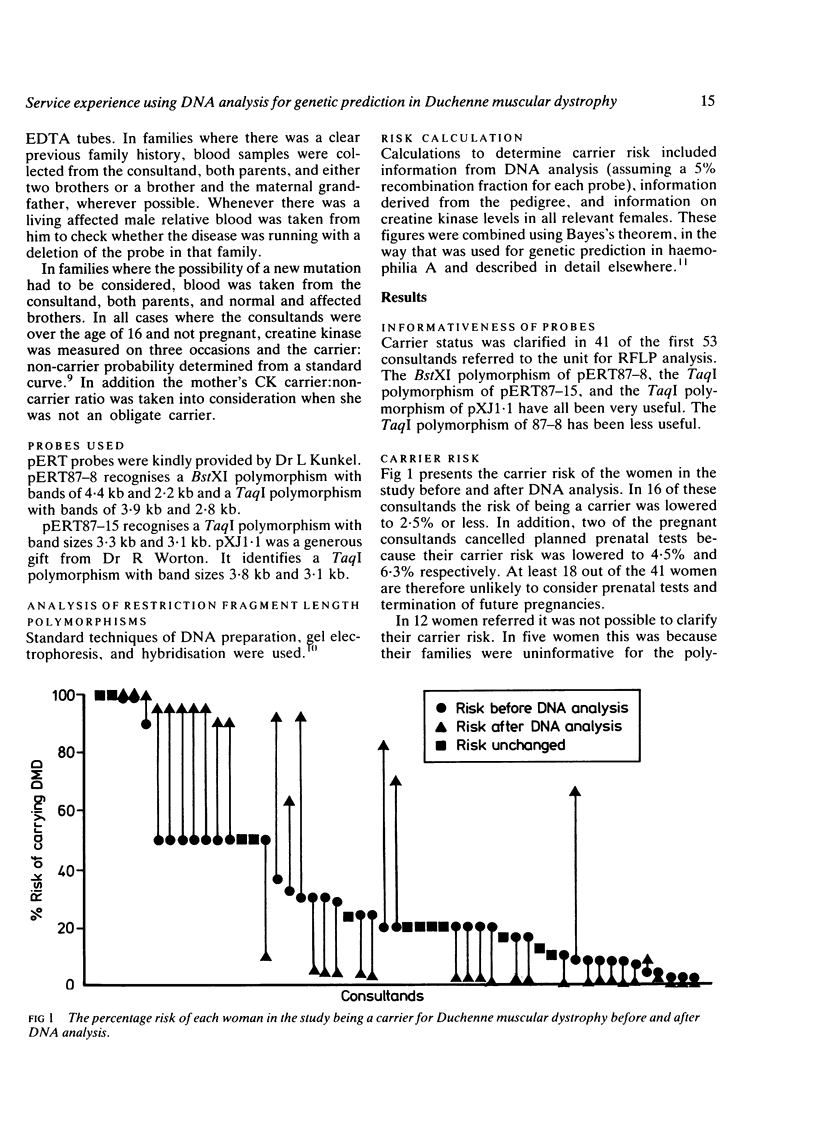
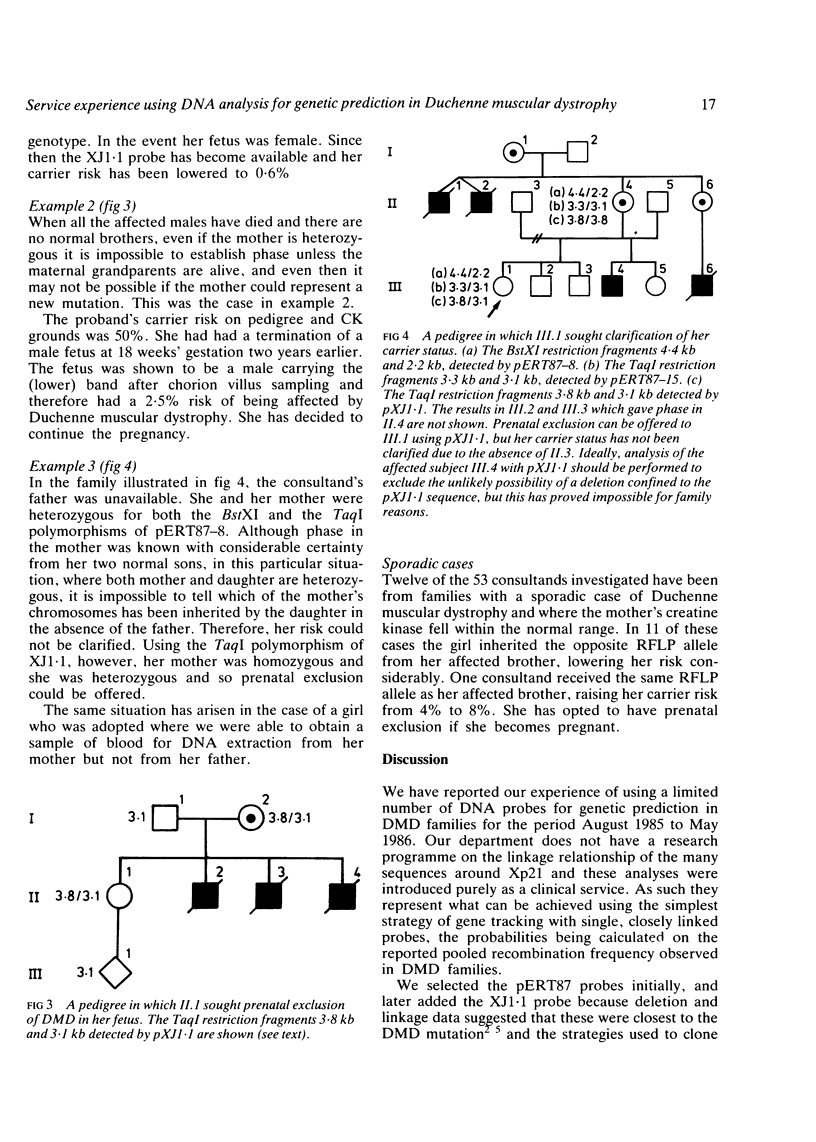
In August 1985 we instituted a carrier and prenatal testing service for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) using direct DNA analysis. The experience over the first nine months is described. We have analysed samples for RFLPs from 154 people including 53 women at risk of being DMD carriers from 37 families. We used the probes pERT87.8 (BstXI and TaqI polymorphisms), 87-15 (TaqI polymorphism), and pXJ1.1 (TaqI polymorphism). Forty-one of the women have had their risks altered. We found one deletion (pERT87-8) out of 23 DNA samples analysed from affected boys. We used a recombination fraction of 0.05 in risk calculations but did not detect any known crossovers. In nine of the families there is only an isolated case of DMD. In families where we have not been able to alter the risk of the women being a carrier (for example, because all brothers are dead), we have offered prenatal exclusion and have carried out one first trimester prenatal diagnosis on this basis. Lowering the risk of an affected fetus to less than 2.5% appears to be a satisfactory situation for many (most) of the women involved and seems to justify the introduction of genetic prediction based on single intragenic probes despite the 5% recombination frequency.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E., Bonten E. J., De Lange L. F., Veenema H., Majoor-Krakauer D., Hofker M. H., Van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. DNA probe analysis for carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a standard diagnostic procedure. J Med Genet. 1986 Dec;23(6):573–580. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.6.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Lehrach H. Long-range restriction map around the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):582–585. doi: 10.1038/324582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Pearson P. L., Harper P. S., Murray J. M., O'Brien T., Sarfarazi M., Williamson R. Linkage analysis of two cloned DNA sequences flanking the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus on the short arm of the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2303–2312. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis N. R., Evans K., Clayton B., Carter C. O. Use of creatine kinase for detecting severe X-linked muscular dystrophy carriers. Br Med J. 1976 Sep 4;2(6035):577–579. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6035.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbeck K. H., Ritter A. W., Tirschwell D. L., Kunkel L. M., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Hejtmancik J. F., Boehm C., Ionasescu V., Ionasescu R. Recombination with pERT87 (DXS164) in families with X-linked muscular dystrophy. Lancet. 1986 Jul 12;2(8498):104–104. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91634-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Hejtmancik J. F., Caskey C. T., Speer A., Monaco A. P., Middlesworth W., Colletti C. A., Bertelson C., Müller U., Bresnan M. Analysis of deletions in DNA from patients with Becker and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):73–77. doi: 10.1038/322073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Bertelson C. J., Middlesworth W., Colletti C. A., Aldridge J., Fischbeck K. H., Bartlett R., Pericak-Vance M. A., Roses A. D., Kunkel L. M. Detection of deletions spanning the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus using a tightly linked DNA segment. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):842–845. doi: 10.1038/316842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Neve R. L., Colletti-Feener C., Bertelson C. J., Kurnit D. M., Kunkel L. M. Isolation of candidate cDNAs for portions of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):646–650. doi: 10.1038/323646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pembrey M. E., Davies K. E., Winter R. M., Elles R. G., Williamson R., Fazzone T. A., Walker C. Clinical use of DNA markers linked to the gene for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Mar;59(3):208–216. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.3.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. N., Belfall B., Duff C., Logan C., Kean V., Thompson M. W., Sylvester J. E., Gorski J. L., Schmickel R. D., Worton R. G. Cloning of the breakpoint of an X;21 translocation associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):672–675. doi: 10.1038/318672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker A., Hart K., Cole C., Hodgson S., Johnson L., Dubowitz V., Bobrow M. Linkage studies in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. J Med Genet. 1986 Dec;23(6):538–547. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.6.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. M., Harper K., Goldman E., Mibashan R. S., Warren R. C., Rodeck C. H., Penketh R. J., Ward R. H., Hardisty R. M., Pembrey M. E. First trimester prenatal diagnosis and detection of carriers of haemophilia A using the linked DNA probe DX13. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Sep 21;291(6498):765–769. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6498.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


