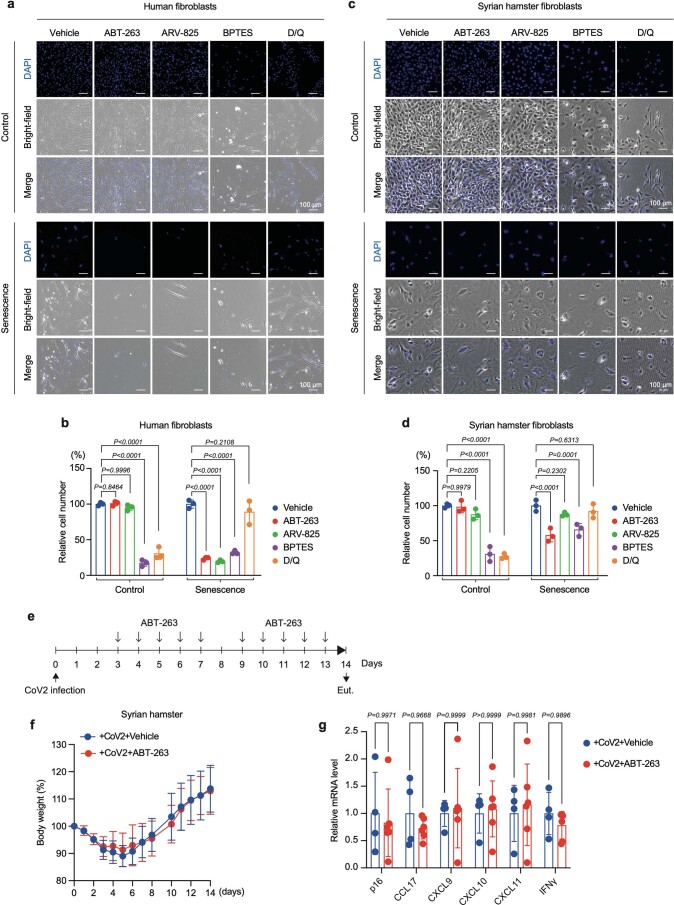
Extended Data Fig. 9. Existing senolytic drugs were ineffective in Syrian hamsters both in vitro and in vivo.
a–d, The early passage human diploid fibroblasts (HDFs) and Syrian hamster fibroblasts (Control) were rendered senescence by treatment with doxorubicin (Senescence) for 9 days. Then, control and senescence human/Syrian hamster fibroblasts were cultured with indicated senolytic drugs (ABT-263; 1 μM, ARV-825; 25 nM, BPTES; 10 μM, dasatinib; 2 μM /quercetin; 20 μM (D/Q)) for 72 hours. Representative photographs of 3 biological replicates were shown (a,c). The relative cell number of 3 biological replicates (vehicle-treatment cells were calculated as 100%) was shown (b and d). e–g, Syrian hamsters were intranasally inoculated with SARS-CoV-2 (B.1.1.7) 5.6 × 105 PFU (in 80 μL), and treated with ABT-263 (100 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle. The timeline of the experiment was shown (e). The body weight were monitored until day 14 (CoV2+vehicle; n = 4, CoV2+ABT-263; n = 6) (f). The senescence-related gene expression at day 14 post-infection by RT-qPCR analysis (CoV2+vehicle; n = 4, CoV2+ABT-263; n = 6) was shown (g). For all graphs, error bars indicate mean ± standard deviation (s.d.).Statistical significance was determined with two-way ANOVA followed by sidak’s multiple comparison test in (b), (d), and (e).