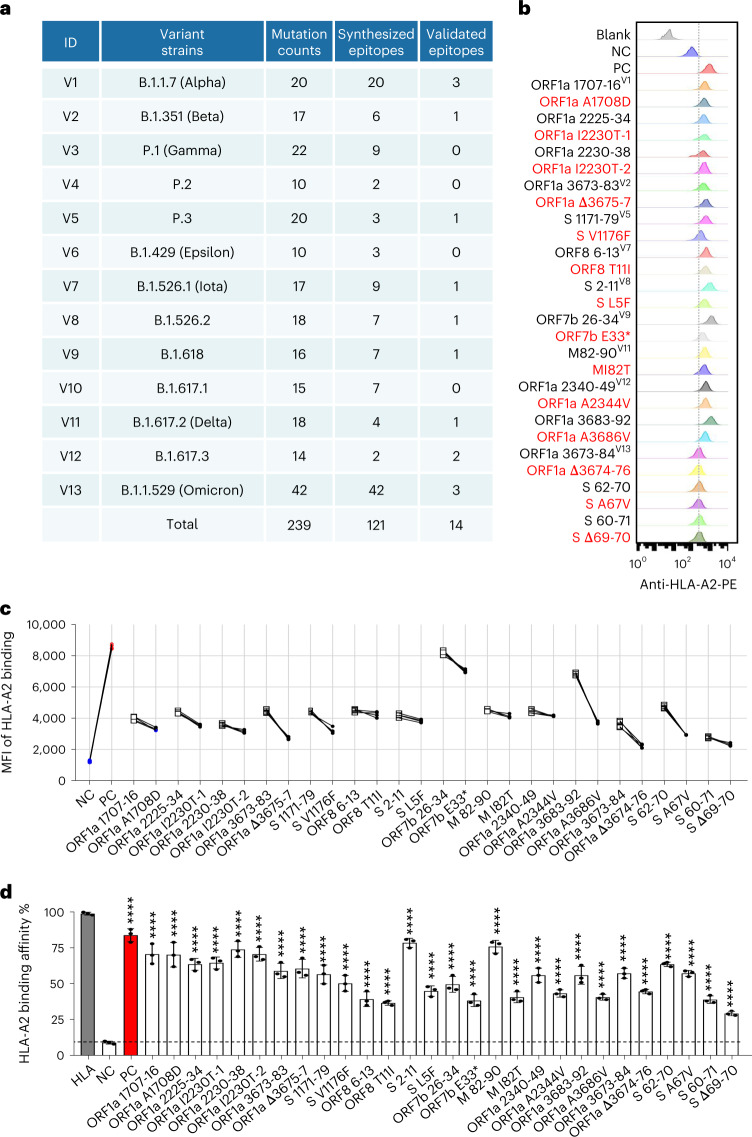
Fig. 2. Identification of HLA-A2-restricted T cell epitopes from SARS-CoV-2 variants.
a, Summary of mutation counts and synthesized and validated epitopes from 13 SARS-CoV-2 variant strains. b,c, Comparison of ancestral and mutant epitope binding affinity to HLA-A2 on T2 cells. Ancestral and mutant epitopes are listed in black and red, respectively, in b. Paired ancestral and mutant epitopes are listed adjacently. Numeric superscripts in b correspond to ID numbers in a. Blank, no peptides; NC, negative control, EBV virus peptide IVTDFSVIK; PC, positive control, influenza A M1 peptide GILGFVFTL. The same applies throughout the paper. d, Evaluation of ancestral and mutant SARS-CoV-2 epitope binding to HLA-A2 by ELISA assay. Data are shown as mean ± s.d., n = 3 independent experiments for each tested epitope. ****P < 0.0001 (two-sided t-test, comparing to NC). Threshold for peptide MHC (pMHC) formation positivity was set as above the average OD value of the negative control. HLA: control UV-sensitive peptide without UV irradiation.