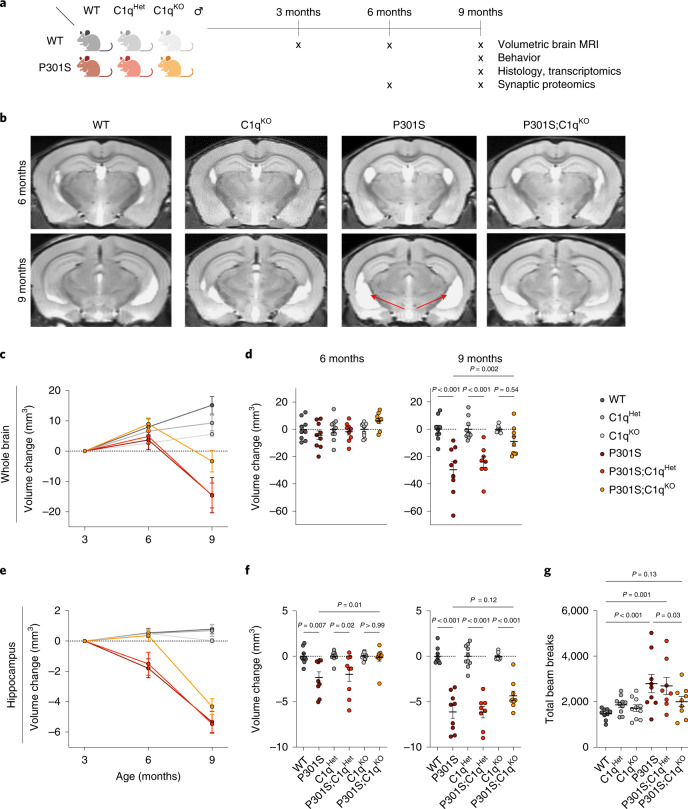
Fig. 1. C1q deletion reduces neurodegeneration in P301S mice.
a, Study design. Male P301S and C1qKO mice were crossed as indicated and analyzed using longitudinal volumetric brain MRI, behavioral hyperactivity and pathological analysis, transcriptomics and synapse proteomics. b, Representative volumetric MRI images in male mice at 6 and 9 months of age. Arrows indicate hippocampal atrophy and ventricle enlargement in P301S mice. c, Longitudinal volumetric MRI quantification of whole brain volume changes in indicated mouse genotypes at 6 and 9 months (normalized to 3 months). d, Whole brain volume changes in indicated mouse genotypes at 6 and 9 months of age. P301S transgenic mice were normalized to non-transgenic mice with the same C1q genotype for comparison. e, Longitudinal volumetric MRI quantification of hippocampal brain volume changes in indicated mouse genotypes at 6 and 9 months (normalized to 3 months). f, Hippocampus volume changes in indicated mouse genotypes at 6 and 9 months of age. P301S transgenic mice were normalized to non-transgenic mice with the same C1q genotype for comparison. g, Nine-month-old mice were evaluated in the open field behavioral test by measuring total beam breaks to assess for behavioral hyperactivity. Each dot represents the values from one mouse. n = 8–10 mice per genotype (c–g). One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multi-comparisons test (d,f) and one-way ANOVA with Fisher’s least significant difference test (g). All data are presented as mean ± s.e.m.