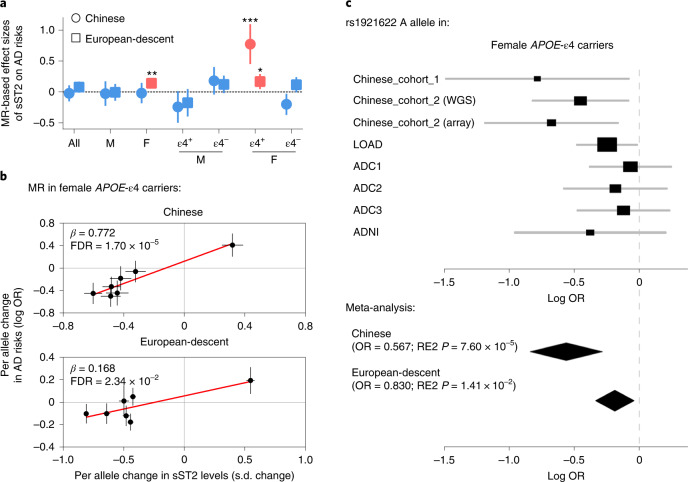
Fig. 4. The rs1921622 A allele is associated with decreased Alzheimer’s disease risk in female APOE-ε4 carriers.
a, Two-sample MR analysis showing the effects of sST2 levels on AD risk in Chinese (circle) and European-descent (box) populations. Circles/boxes and lines indicate the effect sizes of sST2 and 95% CIs in each subgroup, respectively (Supplementary Table 6). Red and blue indicate significant (FDR < 0.05) and nonsignificant (FDR ≥ 0.05) associations, respectively. All, overall population; M, male; F, female; ε4+, APOE-ε4 carriers; ε4−, APOE-ε4 noncarriers. b, Two-sample MR analysis showing the associations between sST2 level and AD risk in female APOE-ε4 carriers in Chinese and European-descent populations. Circles and lines indicate the effect sizes and standard errors of each SNP, respectively. c, Forest plot showing the meta-analysis results of the rs1921622 A allele on AD risk in female APOE-ε4 carriers (n = 912 HCs, n = 1,898 individuals with AD). Rectangles and diamonds denote the effect sizes (log OR) obtained from independent datasets and meta-analysis, respectively. For the independent datasets, horizontal lines indicate 95% CIs, and rectangle size is proportional to the weight used in the meta-analysis. RE2 P, meta-analysis P value using Han and Eskin’s random-effects model. *FDR < 0.05, **FDR < 0.01, ***FDR < 0.001.