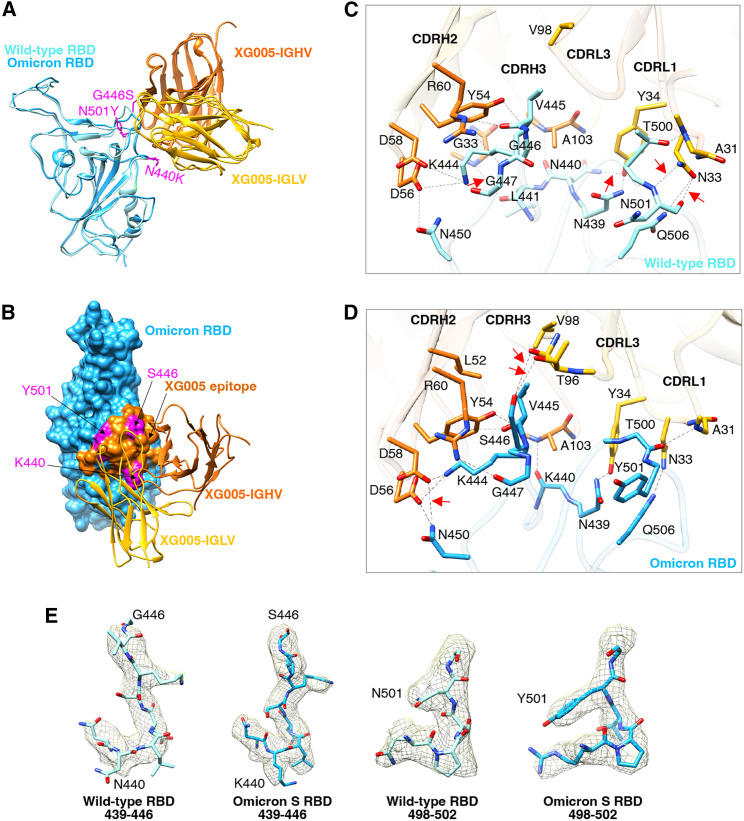
Figure 4.
Comparison the interface between SARS-CoV-2 wild-type RBD-XG005 and Omicron RBD-XG005
(A) Comparison the models of SARS-CoV-2 wild-type RBD-XG005 and Omicron RBD-XG005. Wild-type RBD and Omicron RBD were shown as ribbons and colored in light sky blue and deep sky blue, respectively. The XG005 IGHV and IGLV are colored in orange and yellow, respectively. Omicron mutation residues located in the XG005 epitope are shown as atoms and colored in magenta.
(B) The model of Omicron RBD-XG005. Omicron RBD is displayed in deep sky blue. The XG005 epitope is colored in orange, and Omicron mutation residues within the interface located in XG005 epitope are shown as atoms and colored in magenta.
(C and D) The detailed interfaces between SARS-CoV-2 wild-type RBD and XG005 (C) and between Omicron RBD and XG005 (D). The red arrows emphasize the specific interactions between RBD and XG005.
(E) Density maps of residues around the wild-type RBD-XG005 interface or Omicron RBD-XG005 interface. Density maps were generated by DeepEMhancer. The Omicron mutations located in the XG005 epitope are labeled.