FIGURE 1.
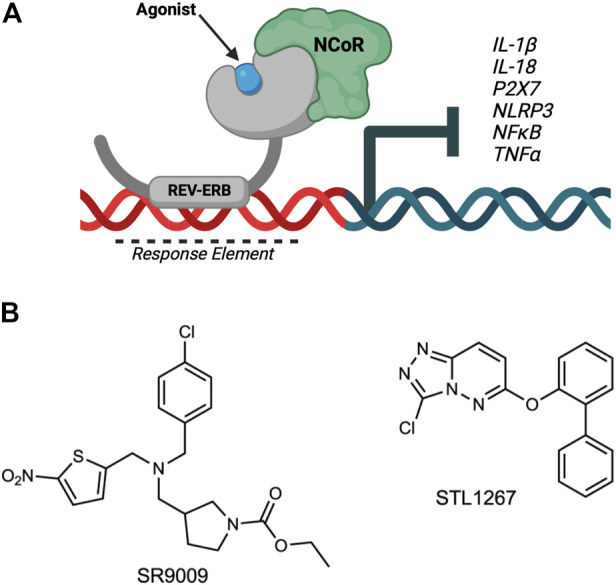
Overview of REV-ERB regulation of inflammatory components involved in pain. (A) The nuclear receptor REV-ERB recognizes sequences within the promoter of its target genes (Response Element) and binds DNA via its DNA-binding domain. Upon binding of a ligand, REV-ERB undergoes a conformational change and recruits the NCoR corepressor, causing the repression of transcription of its target genes including NLRP3, IL-1β, and other pro-inflammatory cytokines and pathway genes. (B) Structures of two REV-ERB agonists: SR9009 and STL1267.
