FIGURE 9.
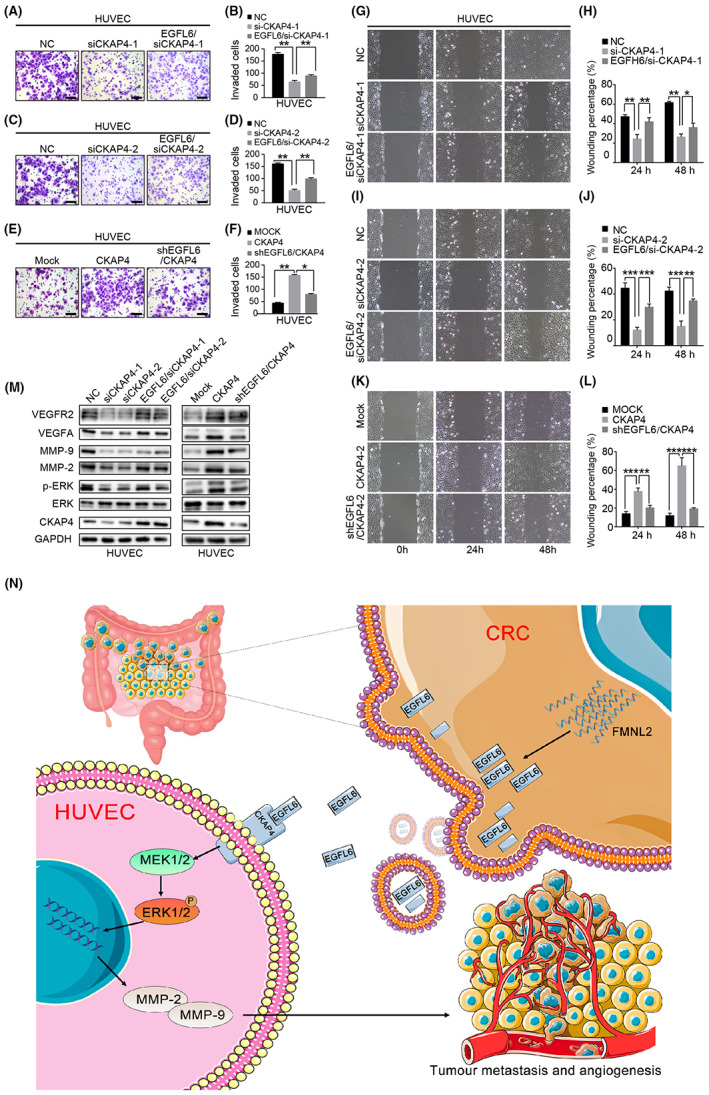
ERK1/2 signaling pathway involved in formin‐like 2 (FMNL2)/epidermal growth factor‐like protein 6 (EGFL6) mediates angiogenesis. (A–D) Transwell migration assay to investigate the effect of cytoskeleton‐associated protein 4 (CKAP4) knockdown, with or without being treated with conditioned medium (CM) from colorectal cancer (CRC) cells, after transfection with EGFL6 overexpression plasmids on the migration ability of HUVECs. (E, F) Transwell migration assay to investigate the effect of CKAP4 overexpression, with or without being treated with CM from CRC cells, after transfection with EGFL6 shRNA plasmids on the migration ability of HUVECs. (G–J) Scratch wound‐healing motility assay was used to observe the changes in the migration of HUVECs after CKAP4 knockdown, with or without stimulation with CM from CRC cells after transfection with EGFL6 overexpression plasmids. (K, L) Scratch wound‐healing motility assay was carried out to observe the changes in the migration of HUVECs after CKAP4 overexpression with or without stimulation with CM from CRC cells after transfection with EGFL6 shRNA plasmids. (M) Western blot assay to detect the expression level of ERK pathway‐related proteins (ERK, p‐ERK, vascular endothelial growth factor A [VEGFA], vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 [VEGFR2], MMP2, and MMP9) in HUVECs with different CKAP4 expression, with or without stimulation with CM from CRC cells with different EGFL6 expression. (N) Briefly, FMNL2 overexpression in CRC cells inhibits EGFL6 degradation by binding with EGFL6 and promotes its secretion. Subsequently, EGFL6 integrates with the HUVEC membrane receptor CKAP4 to activate the ERK1/2 signaling pathway, thereby promoting angiogenesis and metastasis. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM; n = 3 independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. NC, negative control
