Figure 7. Liebenberg syndrome is caused by ectopic Pen-Pitx1 interactions.
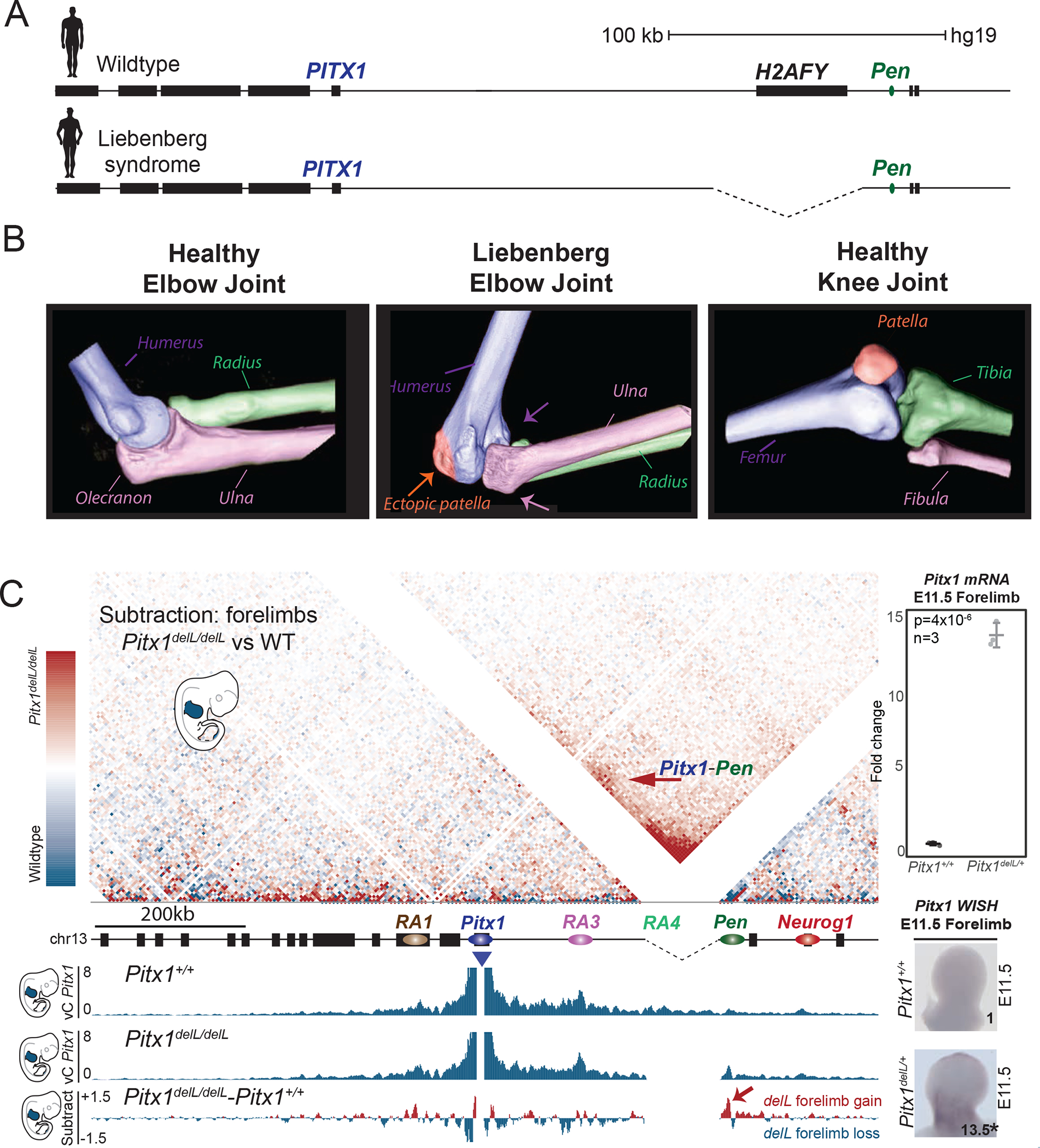
A. Liebenberg syndrome is caused by deletions at the PITX1 locus in human patients. B. 3D CT-scan of healthy human elbow joint, human Liebenberg syndrome elbow joint, and healthy human knee joint. Note that the Liebenberg elbow joint adopts morphologies of the knee-joint. C. The subtraction of wildtype and Pitx1delL/delL cHiC from forelimbs shows gain of interaction between Pitx1 with Pen (red arrow). vC profiles using Pitx1 as a viewpoint derived from cHiC in E11.5 wildtype and Pitx1delL/delL forelimb tissues and the subtraction of both tracks further show the gain of chromatin interaction with Pen (red arrow). Left: Pitx1 WISH and qRT-PCR of Pitx1delL/+ forelimb tissue showing a 13.5-fold ectopic expression (asterisk: we used a one-sided t-test to evaluate the significance of Pitx1 increase and found a p-value=4×10−6; the standard deviation is represented by error bars; the measure of centre is the average of the datapoints; n=3 biologically independent wildtype and mutant forelimb pairs).
