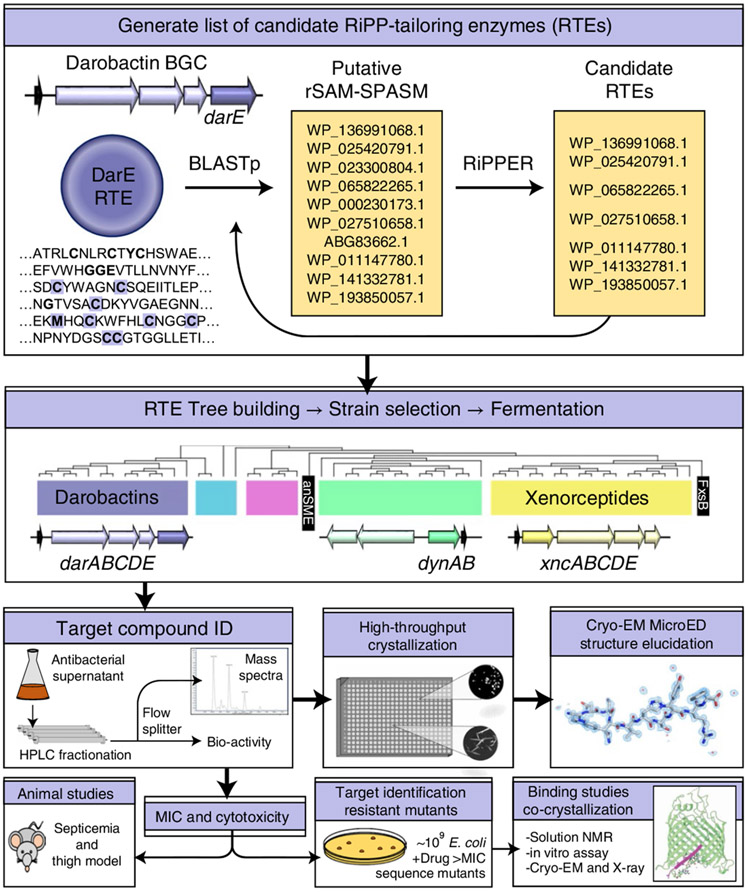
Fig. 1 ∣. Schematic overview of the workflow.
The darobactin operon radical SAM enzyme, DarE, was used to query NCBI BLASTp. BLASTp hits were examined for associations with putative RiPPs in the surrounding genomic neighbourhood using the RiPPER search tool or manual curation, and were applied as further BLASTp queries in such cases. Producers of putatively identified RiPPs were fermented in media to screen for the presence of these RiPPs by biological activity assays or mass spectrometry. Once candidates were identified, these were purified and characterized through both biological assays to determine spectrum of action/cytotoxicity and structural elucidation approaches. A promising compound with low toxicity was then tested for efficacy in animal models of E. coli infection and its mechanism of action identified.