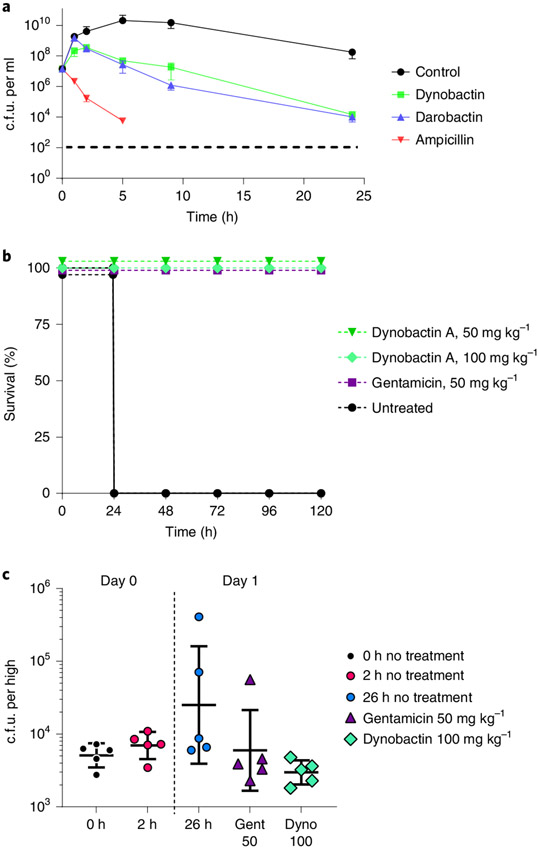
Fig. 5 ∣. Efficacy of dynobactin A.
a, Time-dependent killing of E. coli ATCC 25922 by dynobactin, darobactin and ampicillin. Antibiotics were added at 4x their respective MICs. Time points are graphed as the mean c.f.u. ± s.d. The experiment was performed in biological triplicate. Ampicillin-killed E. coli fell below the limit of detection, denoted by a dashed line. b, Mouse septicaemia model, wherein mice were inoculated with a lethal dose of multidrug-resistant E. coli AR350, followed by administration of a single intraperitoneal dose of antibiotics: dynobactin 50 mg kg−1, dynobactin 100 mg kg−1 and gentamicin 50 mg kg−1 at 1 h post infection; an untreated mouse group was included. Four mice were tested per group. c, In a neutropenic thigh model of E. coli AR350 infection, gentamicin (purple triangle) or dynobactin (green diamond) were delivered to groups of mice (n = 5) by intraperitoneal injection at 2 h post infection (red circle). Infection was monitored over 26 h. At 26 h post infection (blue circle), thighs were homogenized, serially diluted and plated in triplicate for c.f.u. Error bars represent c.f.u. mean ± s.d. for each group.