Figure 2: Alternative hypotheses explaining host susceptibility to infection and colonization with C. auris.
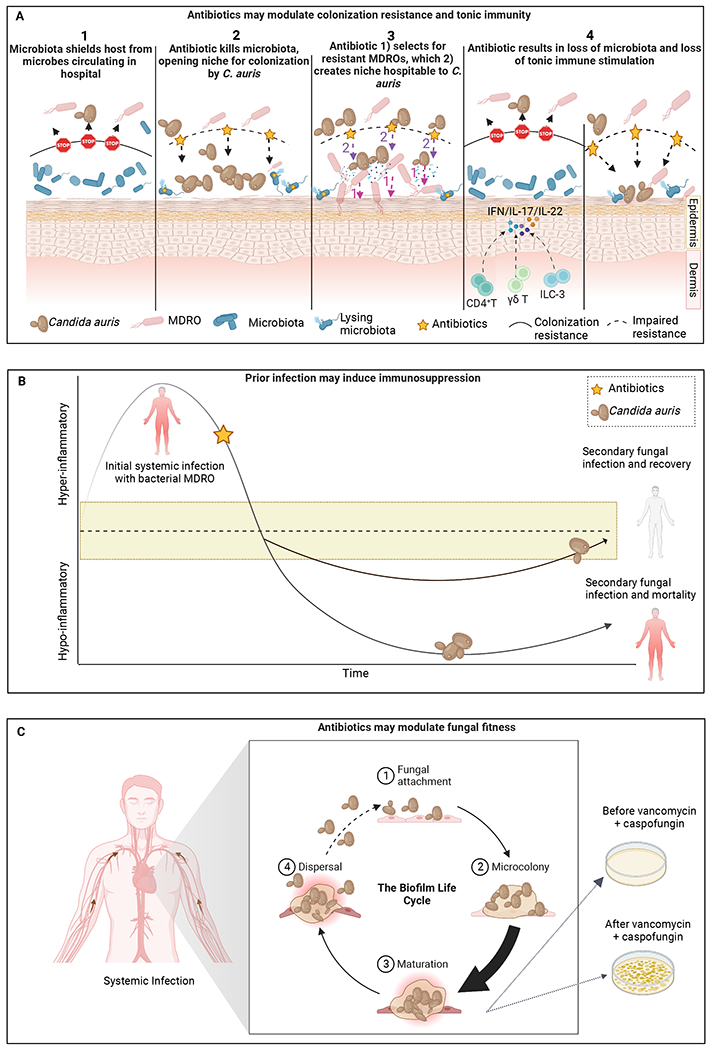
A) Antibiotics may open a niche for C. auris colonization by modulating the commensal microbiota via several potential mechanisms. B) Adapted from117, an initial bout of bacterial sepsis may induce immunosuppression, paving the way for secondary infection and mortality, with antibiotic serving as a red herring. The yellow banding indicates a range of immune-competence. C) Vancomycin and other antibiotics may directly modulate the fitness of C. auris by increasing biofilm formation and inducing a state of tolerance, or via other mechanisms. Created with BioRender.com.
